Block Boundary Suggestion Project - Delineation
The Redistricting Data Program
2025RDP_BBSP_GUPSWeb_UserGuide_NSC_final_approved
Block Boundary Suggestion Project - Delineation
OMB: 0607-0988
2025RDP_BBSP_GUPSWeb_UserGuide_NSC_final_approved
January 2026
This page intentionally left blank.
Table of Contents
SECTION 1. Block Boundary Suggestion Project Overview 1
SECTION 2. Suggested Workflow 3
2.4 Linear Feature Extension Review 6
2.6 Block Boundary Suggestion Flagging 7
2.6.1 Block Boundary Criteria 8
2.6.2 Assigning a “Must Hold” Flag 9
2.6.3 Assigning a “Do Not Hold” Flag 9
2.7 Block Area Grouping Delineation 10
2.9 Potential Small Block Check 10
2.11 Submitting Updates to the Census Bureau 11
SECTION 3. Getting Started 12
3.1 Getting Started with GUPS Web 12
3.1.2 Logging into GUPS Web 12
3.1.3 GUPS Web User Access Roles 13
3.1.3.2 Project Collaborator 13
3.2.4 User Management Module 16
3.3.1 GUPS Web Navigation Bar 20
3.3.4.1 Manual BBSP Change Layers 31
3.3.4.2 Attribute Table Tools 31
3.3.6 Project Management Tool 34
SECTION 4. BBSP Update Activities in GUPS Web 36
4.1.1 Adding a Linear Feature 37
4.1.2 Deleting a Linear Feature 38
4.1.3 Restoring a Deleted Linear Feature 39
4.1.4 Modifying Attributes of a Linear Feature 40
4.1.5 Splitting a Linear Feature 40
4.2.1 Modify Area Feature Tool 41
4.2.2 Boundary Correction by Adding Area to Area Landmark 43
4.2.3 Boundary Correction by Removing Area from an Area Landmark 45
4.2.4 Creating a New Area Landmark 47
4.2.5 Deleting an Area Landmark 48
4.2.6 Modifying the Attributes of an Area Landmark 49
4.3.1 Creating Legal Changes with the Modify Area Feature Tool 51
4.3.2 Adding Area through Legal Changes (Annexation) 54
4.3.3 Removing Area through Legal Changes (Deannexation) 56
4.3.4 Boundary Correction by Adding Area to a Legal Entity 58
4.3.5 Boundary Correction by Removing Area from a Legal Entity 60
4.3.6 Adding a New Legal Entity 62
4.3.7 Deleting a Legal Entity 64
4.3.8 Modifying the Attributes of a Legal Entity 66
4.4 Linear Feature Extension Review 67
4.4.1 Verify Linear Feature Extension Tool 68
4.5.1 Block Size Review Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.6 Block Boundary Suggestion Flagging 70
4.6.1 Block Boundary Criteria 71
4.6.2.1 Assigning “Must Hold” Flags 75
4.6.3 “Do Not Hold” Flags Error! Bookmark not defined.
4.6.3.1 Assigning “Do Not Hold” Flags 77
4.6.4 Removing a “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold” Flag 77
4.6.5 Digitizing a New Linear Feature Extension 77
4.7 Block Area Grouping Delineation 78
4.7.1 Creating a Block Area Grouping 79
4.7.2 Deleting a Block Area Grouping 79
4.9 Potential Small Block Check 81
4.11 Submitting Updates to the Census Bureau 83
4.11.1.2 Download Project Files 86
Appendix A Partnership Shapefile Names and Layouts A-1
Appendix B MTFCC Descriptions B-1
List of tables
Table 1: 2030 Census Planned Tabulation Block Boundaries by MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code (MTFCC) 1
Table 2: MTFCCs for Linear Feature Review 4
Table 3: Block Size Indicator Values 7
Table 4: Description of Block Boundary Flagging Fields 8
Table 5: GUPS Web User Access Roles 13
Table 6: How to Invite a User to GUPS Web Project 17
Table 7: How to Utilize the Manage Users Interface 19
Table 8: GUPS Web Navigation Bar 20
Table 15: Attribute Table Tools 31
Table 16: How to Search the Attribute Table 32
Table 17: Import/Export Tools 34
Table 18: How to Add a Linear Feature 37
Table 19: How to Delete a Linear Feature 38
Table 20: How to Restore a Deleted Linear Feature 39
Table 21: How to Modify a Linear Feature 40
Table 22: How to Split a Linear Feature 41
Table 23: How to Add Area to an Area Landmark 44
Table 24: How to Remove Area from an Area Landmark 46
Table 25: How to Create a New Area Landmark 47
Table 26: How to Delete an Area Landmark 48
Table 27: How to Modify an Area Landmark 49
Table 28: How to Modify an Area Landmark 50
Table 29: How to Perform an Annexation 55
Table 30: How to Perform a Deannexation 57
Table 31: How to Add Area to a Incorporated Place or MCD 59
Table 32: How to Remove Area from an Incorporated Place 61
Table 33: How to Add a New Incorporated Place or MCD 63
Table 34: How to Delete An Incorporated Place 65
Table 35: How to Modify the Attributes of an Incorporated Place or MCD 67
Table 36: How to Review Linear Feature Extensions 68
Table 37: Block Size Indicator Values 69
Table 38: Description of Block Boundary Flagging Fields 70
Table 39: Block Boundary Flagging Symbology 71
Table 40: How to Apply a "Must Hold" Flag 76
Table 41: How to Apply a "Do Not Hold" Flag 77
Table 42: How to Remove a "Must Hold" or "Do Not Hold" Flag 77
Table 43: How to Add a Linear Feature Extension 78
Table 44: How to Create a Block Area Grouping 79
Table 45: How to Delete a Block Area Grouping 79
Table 46: How to Review Block Boundary Flags 80
Table 47: How to Review Potential Small Block Output 82
Table 48: How to Review Boundary Changes 83
Table 49: How to Submit a Project to Census 85
Table 50: How to Download Project Files 86
Table 51: How to Export a Map 88
Table 52: State Shapefile Names A-1
Table 53: County Shapefile Names A-2
Table 54: All Lines (Edges) Shapefile (PVS_25_v2_edges) A-4
Table 55: Area Landmark Shapefile (PVS_25_v2_arealm) A-5
Table 56: Block Area Grouping Shapefile (PVS_25_v2_bag) A-6
Table 57: Census Blocks- 2020 (PVS_25_v2_tabblock2020) A-6
Table 58: Congressional Districts (PVS_25_v2_cd) A-7
Table 59: Counties and Equivalent Areas (PVS_25_v2_county) A-8
Table 60: Minor Civil Divisions (PVS_25_v2_mcd) A-8
Table 61: Faces (PVS_25_v2_faces) A-9
Table 62: Water (PVS_25_v2_water) A-11
Table 63: Incorporated Place (PVS_25_v2_place) A-11
Table 64: State Legislative Districts (Upper/Senate) (PVS_25_v2_sldu) A-12
Table 65: State Legislative Districts (Lower/House) (PVS_25_v2_sldl) A-13
Table 66: American Indian/Alaska Native Areas (PVS_25_v2_aial) A-14
Table 67: School Districts - Elementary (PVS_25_v2_elsd) A-15
Table 68: School Districts- Secondary (PVS_25_v2_scsd) A-16
Table 69: School Districts- Unified (PVS_25_v2_unsd) A-17
Table 70: Census Block Groups (PVS_25_v2_bg) A-18
Table 71: Census Tracts- 2020 (PVS_25_v2_tracts2020) A-18
Table 72: Census Designated Places (PVS_25_v2_cdp) A-19
Figure 1: Suggested Workflow 3
Figure 2: Workflow for Accessing GUPS Web 12
Figure 3: GUPS Web Dashboard Button 14
Figure 4: GUPS Web Dashboard Interface 14
Figure 5: Example of Access Denied Message 15
Figure 6: Example of a New Project Opened in GUPS Web (Map View) 16
Figure 7: User Management Module Button 16
Figure 8: Invite Users Interface (County-Level) 17
Figure 9: Invite Users Interface (State-Level) 18
Figure 10: Manage Users Interface 18
Figure 11: GUPS Web Map View with Tools Identified 20
Figure 12: Quick Tools Button 21
Figure 14: View Tools Option 23
Figure 15: Imagery Tools Option 24
Figure 16: Selection Tools Option 25
Figure 17: Edit Tools Option 26
Figure 18: Review Tools Option 28
Figure 19: Layer Legend Button 29
Figure 20: Layer Legend Interface 30
Figure 21: Import/Export Button 33
Figure 22: Import/Export Interface 33
Figure 23: Project Management Button 34
Figure 24: Delete Project Button 34
Figure 25: Notification Button 34
Figure 26: User Count Button 35
Figure 27: Add Linear Feature Button 37
Figure 28: Add Linear Feature Dialog Window 37
Figure 29: Delete/Restore Linear Feature Button 38
Figure 30: "Must Hold" Delete Warning 39
Figure 31: Delete Linear Feature Warning 39
Figure 32: Modify Linear Feature Button 40
Figure 33: Modify Linear Feature Interface 40
Figure 34: Split Linear Feature Button 40
Figure 35: Modify Area Feature Tool Button 41
Figure 36: Modify Area Feature Interface 42
Figure 37: Modify Area Feature Button 43
Figure 38: Modify Area Feature Tool Boundary Correction- Add Area Interface 44
Figure 39: Modify Area Feature Tool Boundary Correction- Remove Area Interface 45
Figure 40: Modify Area Feature Tool New Area Landmark Interface 47
Figure 41: Modify Area Feature Tool Delete Area Landmark Interface 48
Figure 42: Modify Area Feature Tool Modify Attributes Interface 49
Figure 43: Modify Area Feature Tool Modify Attributes Interface 50
Figure 44: Modify Area Feature Tool Interface with Legal Fields 52
Figure 45: Modify Area Feature Tool Annexation Interface 54
Figure 46:Modify Area Feature Tool Deannexation Interface 56
Figure 47: Modify Area Feature Legal Update Boundary Correction-Add Area Interface 58
Figure 48:Modify Area Feature Legal Update Boundary Correction-Remove Area Interface 60
Figure 49: Add a New Legal Entity Interface 62
Figure 50: Delete a Legal Entity Interface 64
Figure 51: Modify Attributes of a Legal Entity Interface 66
Figure 52: Verify Linear Feature Extension Tool Button 68
Figure 53: Verify Linear Feature Extension Tool Interface 68
Figure 54: Feature Flagging Tool Button 75
Figure 55: Feature Flagging Tool Interface 76
Figure 56: Add Linear Feature Extension Button 78
Figure 57: Create Block Area Grouping Button 79
Figure 58: Delete Block Area Grouping Button 79
Figure 59: Block Boundary Review Button 80
Figure 60: Block Boundary Review Interface 80
Figure 61: Potential Small Block Check Button 81
Figure 62: Potential Small Block Check Interface 82
Figure 63: Boundary Review Button 82
Figure 64: Boundary Review Selection Interface 83
Figure 65: Boundary Review Tool Interface 83
Figure 66: Import/Export Button 84
Figure 67: Submit to Census Interface 85
Public Law (P.L.) 94-171 stipulates that the U.S. Census Bureau work in a nonpartisan manner with the states to identify and provide the small-area population counts necessary for legislative redistricting. The Census Bureau is required to provide these counts within one year of Census Day, to the governor and the officers or public bodies responsible for redistricting in each state. For the 2030 Census, the Census Bureau must deliver the counts by April 1, 2031.
The Redistricting & Voting rights Data Office (RVDO) implements the requirements of P.L. 94-171 through the Redistricting Data Program (RDP) which is organized into five phases for the 2030 Census:
Phase 1: Block Boundary Suggestion Project (BBSP)
Phase 2: Voting District Project (VTDP)
Phase 3: Delivery of the 2030 Redistricting Data
Phase 4: Collection of Post-2030 Census Congressional and State Legislative District Plans
Phase 5: Review of the 2030 Census Redistricting Data Program and Recommendations for the 2040 Census
This document pertains to Phase 1: Block Boundary Suggestion Project (BBSP) of the RDP. Through the BBSP, nonpartisan liaisons designated by the governors and legislative leadership in each state, the District of Columbia, and the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, can influence the delineation of the 2030 Census tabulation blocks (i.e., blocks).
Participants influence block delineation by suggesting linear features (e.g., roads, rivers, railroads, property lines) or edges to be held or not held as block boundaries. The Census Bureau refers to this as suggesting block boundaries, or setting or flagging ‘Must Hold’ or ‘Do Not Hold’ on the features. Participants can also influence block boundaries by adding and deleting linear features or edges, and by suggesting updates to boundaries for other census geographies including incorporated places, minor civil divisions (MCDs), counties, and area landmarks, all of which are potential block boundaries.
SECTION 1 of the document provides the conceptual overview of the planned 2030 Census tabulation block boundaries.
SECTION 2 of the document contains the suggested workflow, update activities, and quality control activities.
SECTION 3 of the document contains instructions for getting started with the GUPS Web application.
SECTION 4 of the document contains detail on performing BBSP Update Activities and how to submit files to the Census Bureau via GUPS Web.
Block boundaries primarily follow visible features, such as roads and rivers, as well as any edges that bound legal, administrative, or statistical geographic areas or selected area landmarks stored in the Master Address File/Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing (MAF/TIGER) System (MTS). Census blocks nest within all other tabulated census geographic entities and are the smallest tabulation geography published by the decennial census.
Table 1: 2030 Census Planned Tabulation Block Boundaries by MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code (MTFCC) lists the feature and boundary types currently planned as 2030 Census block boundaries. If state participants flag these features as a “Do Not Hold” (i.e., request that the feature or boundary type not become a 2030 block boundary), the Census Bureau may not accept the “Do Not Hold” suggestion.
Table 1: 2030 Census Planned Tabulation Block Boundaries by MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code (MTFCC)
MTFCC |
Description |
MTFCC |
Description |
G2120 |
Hawaiian |
G5200 |
Congressional District |
G2130 |
Alaska Native Village Statistical Area |
G5210 |
State Legislative District (Upper Chamber) |
G2140 |
Oklahoma Tribal Statistical Area |
G5220 |
State Legislative District (Lower Chamber) |
G2150 |
State-designated Tribal Statistical Area |
G5240 |
Voting District |
G2160 |
Tribal Designated Statistical Area |
G5400 |
Elementary School District |
G2170 |
American Indian Joint Use Area |
G5410 |
Secondary School District |
G2200 |
Alaska Native Regional Corporation |
G5420 |
Unified School District |
G2300 |
Tribal Subdivision |
G6330 |
Urban Growth Area |
G2400 |
Tribal Census Tract |
G6500 |
Military Installation |
G2410 |
Tribal Block Group |
K2181 |
National Park Service Land |
G4000 |
State or State Equivalent |
K2182 |
National Forest or Other Federal Land |
G4020 |
County or County Equivalent |
K2540 |
University or College |
G4040 |
County Subdivision |
K1235 |
Juvenile Institution |
G4060 |
Sub-Minor Civil Divisions |
K1236 |
Local Jail or Detention Center |
G4110 |
Incorporated Place |
K1237 |
Federal Penitentiary, State Prison, or Prison Farm |
G4120 |
Consolidated City |
K1238 |
Other Correctional Institution |
G5020 |
Census Tract |
S1100 |
Primary Road |
G5035 |
Block Area Grouping |
S1200 |
Secondary Road |
While primary and secondary roads (i.e., MTFCCs S1100 and S1200) are planned block boundaries, other linear features, such as local roads, alleys, railroads, and perennial water, may or may not qualify as block boundaries based on the established criteria. These features can be flagged as “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold” block boundaries.
Participants can determine whether a feature is a planned block boundary by the feature’s value in the Census Block Boundary Flag (CBBFLG) field in the attribute table of the All Lines (edges) shapefile. A CBBFLG value of “4” indicates the feature is a planned 2030 block boundary, while a CBBFLG value of “9” indicates the feature is ineligible as a 2030 block boundary. When the CBBFLG field is null, its status has not yet been determined. This indicates that it is a good candidate for a “Must Hold” or a “Do Not Hold” flag.
Figure 1 depicts the suggested workflow for reviewing and updating Census Bureau data for the BBSP. This section outlines the activities associated with each of the workflow process boxes.
Work is performed at a county level and should be submitted to the Census Bureau on a flow basis, as each county is completed. Submitting work on a flow basis permits the RVDO and the Census Bureau to review the files early in the process, provide feedback as necessary, and facilitates file processing.
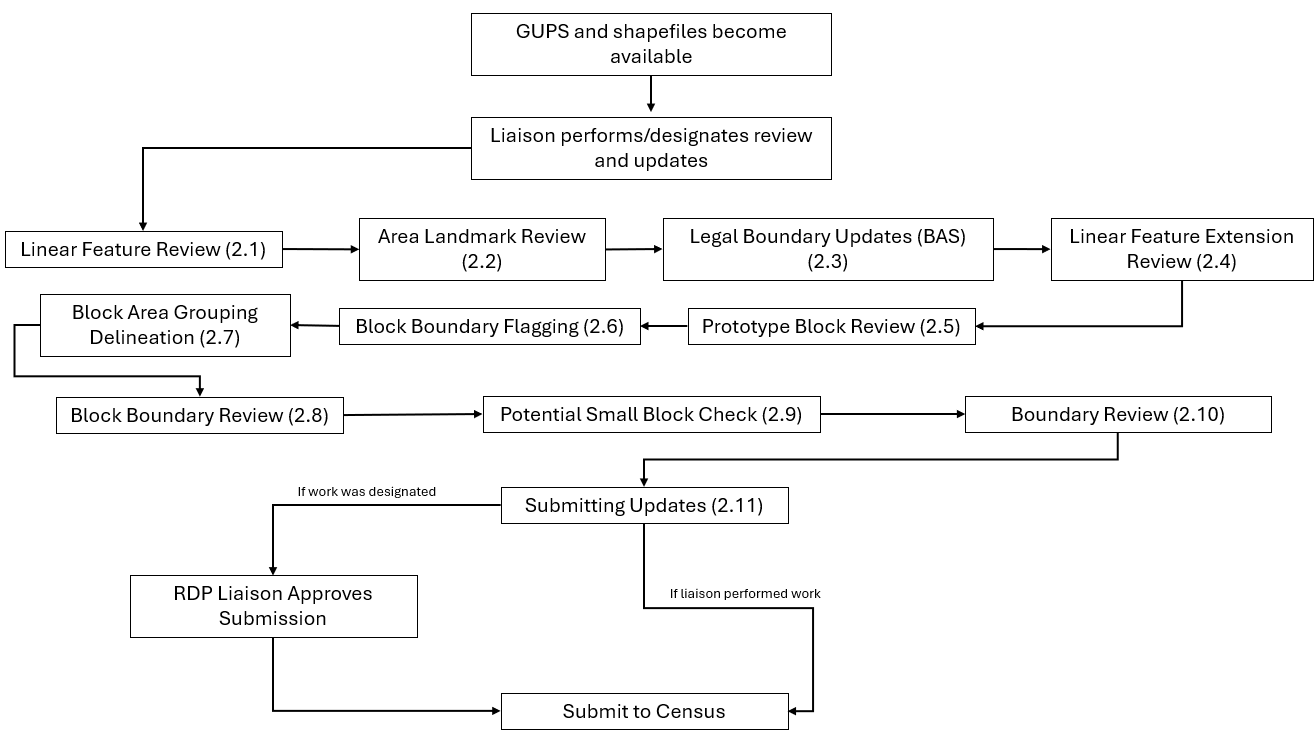
Note: The review process may be different for each state. The number in parentheses refers to the section where the action is described.
Review the Census Bureau’s linear features (edges shapefile) to determine whether there are features that need to be added or deleted. Pay particular attention to any areas that have experienced population growth, and where there may be new housing or subdivisions not reflected in the Census Bureau’s geospatial data.
Table 2: MTFCCs for Linear Feature Review
MTFCC |
Description |
MTFCC |
Description |
C3024 |
Levee |
L4165 |
Ferry Crossing |
C3027 |
Dam |
P0001 |
Nonvisible Legal/Statistical Boundary |
H3010 |
Stream/River |
P0002 |
Perennial Shoreline |
H3013 |
Braided Stream |
P0003 |
Intermittent Shoreline |
H3020 |
Canal, Ditch, or Aqueduct |
P0004 |
Other non-visible bounding edge (e.g., Census water boundary, boundary of area feature) |
K2432 |
Pier/Dock |
S1100 |
Primary Road |
K2459 |
Runway/Taxiway |
S1200 |
Secondary Road |
L4010 |
Pipeline |
S1400 |
Local Neighborhood Road, Rural Road, City Street |
L4020 |
Power Line |
S1500 |
Vehicular Trail (4WD) |
L4110 |
Fence Line |
S1630 |
Ramp |
L4121 |
Ridge Line |
S1640 |
Service Drive usually along a limited access highway |
L4125 |
Cliff/Escarpment |
S1730 |
Alley |
L4130 |
Point-to-Point Line |
S1740 |
Private Road for service vehicles (logging, oil fields, ranches, etc.) |
L4140 |
Property/Parcel Line |
S1820 |
Bike Path or Trail |
R1011 |
Railroad Feature (Main, Spur, or Yard) |
R1051 |
Carline, Streetcar Track, Monorail, Other Mass Transit Rail |
R1052 |
Cog Rail Line, Incline Rail Line, Tram |
|
|
The basic groupings of the MTFCCs are as follows:
S-class = Roads.
R-class = Railroads.*
P-class = Nonvisible Features.*
L-class, K-class, and C-class = Other Linear Features. *
H-class = Hydrography.*
The Census Bureau will also accept attribute updates (name and classification code) for MTFCCs in the S-class (roads). Added road features (except for highway ramps) require a feature name.
*These types of linear features should only be added if desired as a block boundary and therefore must have a “Must Hold” flag assigned to them when submitted to the Census Bureau.
Note: Please be aware that the Census Bureau will not process the wholesale spatial realignment of features merely to conform to an alternate spatial accuracy. If a feature is in the incorrect location in the Census Bureau’s feature network, mark the feature for deletion and then add it in the correct location. Take this action only if most of the realigned feature is more than 7.6 meters from the existing feature or interferes (is topologically incorrect) with relationships to other features.
The Census Bureau accepts updates to area landmarks (e.g., prison areas, state parks, and cemeteries) as part of the BBSP. Allowable updates include:
Boundary corrections (adding and removing area).
Creating a new area landmark.
Removing an area landmark.
Changing or adding a name of an area landmark.
Changing or updating the MTFCC of an area landmark.
If the state plans to reallocate prisoners during redistricting, consider reviewing the existing area landmarks with MTFCCs K1235, K1236, K1237, and K1238, which represent areas with potential prison populations, or create new landmarks for those types of areas.
To report updates to water area features, such as lakes or reservoirs, please contact the RVDO at 301-763-4039 or email <rdo@census.gov>.
Participants may provide legal boundary updates (annexations, deannexations, incorporations and disincorporations), along with their supporting documentation, and boundary corrections. The Census Bureau will assume the responsibility for reconciling the updates with the appropriate governments as part of the Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS).
Participants may submit legal boundary updates for counties, MCDs, and incorporated places. Although legal documentation (effective date, authority type, and documentation number) is not required for boundary updates submitted through the BBSP, the Census Bureau strongly encourages the submission of documentation to expedite our ability to reconcile and process any legal updates reported. Annexations and deannexations without supporting documentation should be submitted as boundary corrections. To report a new county, MCD, or incorporated place without supporting documentation or to delete an existing MCD or county, please call the RVDO at 301-763-4039, or email <rdo@census.gov>.
Note: The Census Bureau cannot guarantee these updates will be made, as we may first have to adjudicate and receive concurrence for the updates from the official BAS contact.
All block boundary suggestions are contingent upon the lines intersecting to form a closed polygon at the time the Census Bureau creates blocks. As a result, all block boundary “Must Hold” flags when combined with the features identified as planned holds, should form a closed polygon.
For the 2020 Census, BBSP participants could place a “Must Hold” flag on an existing feature that did not form a closed a polygon. To do this, the participant also added a feature extension to close the polygon and create a potential new block. Those 2020 feature extensions are included in the 2030 BBSP files for review and update.
The Census Bureau requests that participants review the 2020 linear feature extensions to determine if they are still needed. Please be aware that to hold an old 2020 feature extension as a 2030 block boundary, participants must take an action to again classify that extension as a “Must Hold” suggestion, as described in section 4.6.2.
During the linear feature extension review, participants may:
Hold the old 2020 linear feature extension as a 2030 block boundary suggestion along with the feature from which the extension originates. If possible, when applying a Must Hold to a feature extension, review the extension against cadastral data or imagery to ensure it is in the most appropriate location.
Flag the old 2020 feature extension as a "Do Not Hold". Some linear features cannot be deleted from the MTS. By flagging the old 2020 linear feature extension as a "Do Not Hold", it will help the Census Bureau ensure the feature extension no longer serves as a block boundary.
Ignore the 2020 linear feature extension. If no action is taken on a 2020 linear feature extension, the Census Bureau may delete the old extension or if kept, decide whether to hold the extension and the feature associated with it as a 2030 block boundary or not.
The prototype block shapefile shows what the planned 2030 blocks would look like if created using the geography as it exists at this time. The prototype block shapefile is a useful tool for participants to review their potential block geography and then use the “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags to make targeted updates.
In the prototype block shapefile, the Census Bureau assigned a block size indicator (BLKZIND field) to each block based on the range of the estimated number of housing units in the prototype block. These values can be used to identify both potentially small population blocks and large population blocks to split or merge using the “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags.
Note: Although discrete numbers have been established to assign each block a size value, the actual number of housing units in a block is approximate.
Block size indicators range from “A” through “I”, with “A” blocks having the most housing units and “I” having the least. Prototype blocks estimated to contain no housing units are assigned an indicator letter of “Z.”
Table 3: Block Size Indicator Values
Indicator |
Approximate Number of Housing Units |
A |
Greater than 2,000 |
B |
1,600-1,999 |
C |
1,200-1,599 |
D |
1,000-1,199 |
E |
700-999 |
F |
480-699 |
G |
400-479 |
H |
240-399 |
I |
1-239 |
Z |
Potential “0” housing unit block |
In the prototype block shapefile, the Census Bureau also calculated a shape index (SHAPEIDX) using a simple area to perimeter ratio method. The shape index value will be between 0 and 1. The closer the value to 1, the more compact the block. The closer the value to 0 the less compact the block. These values can be used to help identify less compact blocks to see if their shape would interfere with the ability to conduct redistricting (e.g. long sinuous water bodies). Then, the “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags can be used to remedy this if it is an issue.
BBSP participants can assign BBSP flags to features--suggest they be held or not held as block boundaries--in the BBSP_2030 field of the edges shapefile. Using established criteria for delineating tabulation blocks, the Census Bureau has identified features already planned as 2030 block boundaries, which have a CBBFLG value of “4” in the edges shapefile. Refer to Table 1 for the complete planned feature list. The planned block boundaries may change if the criteria change, or if a feature’s attributes are updated through other Census programs.
The Census Bureau has identified features that are ineligible to be 2030 block boundaries with a CBBFLG value of “9” in the edges shapefile. There are also features with no block boundary status assigned (CBBFLG value is null). Participants are not required to assign a BBSP flag (e.g., “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold”) to every feature in the file, nor should they.
Table 4: Description of Block Boundary Flagging Fields
Values |
Description |
BBSPFLG=1 |
2020 Participant Identified Must Hold Block Boundary |
BBSPFLG=2 |
2020 Participant Identified Do Not Hold Block Boundary |
BBSPFLG=4 |
2020 Census Identified Planned Block Boundary |
BBSPFLG=9 |
2020 Census Identified Ineligible Block Boundary |
BBSP_2030=1 |
2030 Participant Identified Must Hold Block Boundary (Will be null until set by participant) |
BBSP_2030=2 |
2030 Participant Identified Do Not Hold Block Boundary (Will be null until set by participant) |
CBBFLG=1 |
2030 Participant Identified Must Hold Block Boundary (Populated by Census Bureau during processing of BBSP submission. The field will be populated for BBSP Verification and future update cycles. Corresponds to value from the BBSP_2030 field.) |
CBBFLG=2 |
2030 Participant Identified Do Not Hold Block Boundary (Populated by Census Bureau during processing of BBSP submission. The field will be populated for BBSP Verification and future update cycles. Corresponds to value from the BBSP_2030 field.) |
CBBFLG=4 |
2030 Census Identified Planned Block Boundary |
CBBFLG=9 |
2030 Census Identified Ineligible Block Boundary |
All BBSP participant-provided 2030 Census “Must Holds,” i.e., BBSP_2030 = 1, combined with existing features and other planned block boundaries, must form closed polygons.
2030 Census planned block boundaries, i.e., CBBFLG = 4, are an indication of what the Census Bureau plans to use as a 2030 Census block boundary if they were defined today. The planned block boundaries may change if the criteria changes, or if the feature attributes are updated through other Census programs.
BBSP participant-provided 2030 Census “Do Not Holds”, i.e., BBSP_2030 = 2, will not be honored if the line they are placed on needs to be held for other purposes. For example, if a “Do Not Hold” flag was placed on an incorporated place boundary, the “Do Not Hold” flag would not be honored.
Participants may assign a “Must Hold” flag to features to suggest them as 2030 block boundaries. Candidates for assigning a “Must Hold” flag are:
Newly added features.
Features not currently planned as block boundaries.
To ensure features planned as 2030 block boundaries are held should the Census Bureau change their “planned” status.
Participants may wish to assign a “Must Hold” flag to features that are planned 2030 block boundaries in case the block definition criteria or feature classification codes change between when BBSP occurs and when the Census Bureau creates the 2030 Census blocks. Assigning a “Must Hold” flag to a planned block boundary feature will increase the likelihood that the feature will become a 2030 block boundary.
Be aware that assigning a “Must Hold” flag to a feature that is ineligible to be a block boundary or assigning a “Do Not Hold” flag to a feature that is planned to be a 2030 block boundary does not ensure that the Census Bureau will honor the request. The Census Bureau will re-evaluate the feature’s status based on the participant’s suggestion.
All “Must Hold” flags are contingent upon the features intersecting to form a closed polygon at the time the Census Bureau creates the 2030 blocks.
To hold a feature as a 2030 block boundary when the feature does not form a closed polygon, add a feature extension to close the polygon. Feature extensions must meet the following criteria:
Extensions, combined with other features and planned holds, must form a closed polygon.
Extensions must be no longer than 300 feet. (If an extension needs to be longer than 300 feet, participants must provide justification.)
Extensions must be a straight line originating from the end of a road feature.
Extensions must terminate on a non-road feature, except for highways (i.e., extensions may terminate on highways – MTFCC S1100).
Participants may assign “Do Not Hold” flags to features that they do not want to become 2030 block boundaries. Potential candidates for assigning a “Do Not Hold” flag may include:
Private roads, trails, and unimproved roads.
Hydrographic features with no area, shown as a single-line feature, such as streams or creeks.
Any feature creating unnecessary blocks, such as highway ramps, traffic circles, or cul-de-sacs shown as open circles or “lollipops” in the Census geospatial files, and similar features.
Be aware that assigning a “Do Not Hold” flag to a feature that is a 2030 planned block boundary may not be honored if that boundary is needed to meet other Census criteria or program needs. For example, if a “Do Not Hold” flag is placed on an incorporated place boundary, the “Do Not Hold” will not be honored.
During the 2030 Census block creation, the Census Bureau will automatically group islands to form a single block if they have no road features and the islands fall within a 5-kilometer radius. Participants may also choose to group specific islands to create a single 2030 Census block, called a Block Area Grouping (BAG). The criteria for creating a BAG are as follows:
BAG must consist of two or more islands.
BAG perimeter must be entirely over water.
BAGs cannot overlap.
BAGs cannot cross the boundary of other tabulation geographies, such as county or incorporated place boundaries.
BAG delineation is optional, and most appropriate for states with hydrographic areas that contain many islands.
Block boundary suggestions must be reviewed at least once before submitting updates to the Census Bureau. The Block Boundary Review Tool allows participants to systematically navigate to features on the map, by 2030 “Most Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags, for review and further update if desired.
The Potential Small Block Check reviews the edges within the project and returns a list of potential small blocks that exist in the project based on the planned and suggested block boundaries.
All small blocks under 3,000 square meters are identified and listed. Within this list of potential small blocks:
Type “ - “: Small blocks under 3,000 square meters that are created by the planned block boundaries and do not include “Must Hold” flags.
Type A: Small blocks of 500 square meters or less that have one or more bounding edges where a "Must Hold" flag is involved.
Type B: Small blocks of 500.1 square meters to 3,000 square meters that have one or more bounding edges where a "Must Hold" flag is involved.
If the small blocks are unwanted or unintentional, they can be adjusted through Block Boundary Suggestion Flagging (i.e., remove the “Must Hold” flag from a bounding edge or apply a “Do Not Hold” flag). Potential small blocks must be reviewed at least once before submitting updates to the Census Bureau.
The Boundary Review Tool allows updates to area landmarks and legal entities (incorporated places and MCDs) to be viewed. Records can be selected to navigate from update to update. In addition, legal information for annexations and deannexations can be added via the Boundary Review Tool.
The Census Bureau conducts the RDP activities through the official liaison appointed by the governor and legislative leadership of the state. The official liaisons are responsible for making BBSP updates and submitting the projects to the Census Bureau. However, the official liaisons have two options for designating technical liaisons to assist them in making BBSP updates on behalf of the state.
Option 1. Official liaisons can formally designate technical liaisons who are able to perform geographic updates and submit completed updates to the Census Bureau on their behalf. Official liaisons should reach out to the RVDO at 301-763-4039 or <rdo@census.gov> to make technical liaison designations.
Option 2. Official liaisons can delegate work to designees who perform the updates and submit the updates back to the official liaison. The official liaison will submit the work to the Census Bureau if they approve the work. If the official liaison determines that BBSP work completed by a designee requires changes or additional work, it is the official liaison's responsibility to decide whether to make the changes or return the project to their designee for further updates.
The liaison responsible for submitting updates to the Census Bureau should submit completed, county-level files on a flow basis to the Census Bureau directly through GUPS Web. Do not hold files to submit all at once. Submit files as they are completed, especially at the beginning of the update period, so that the Census Bureau can provide feedback if there are errors, omissions, or other concerns.
GUPS Web is a user-friendly geographic information system (GIS) that is customized for each of the Census Bureau’s geographic partnership programs. GUPS Web features a BBSP module which offers tools specific to BBSP that allow participants to create a standardized submission.
Standardized submissions allow the Census Bureau to easily process returned BBSP files and update the MTS. GUPS Web also allows project sharing, collaboration, and the ability to receive feedback from RVDO staff before submitting the project to the Census Bureau.
This section goes into further detail on accessing GUPS web, but a general workflow for accessing GUPS Web is shown in Figure 2.
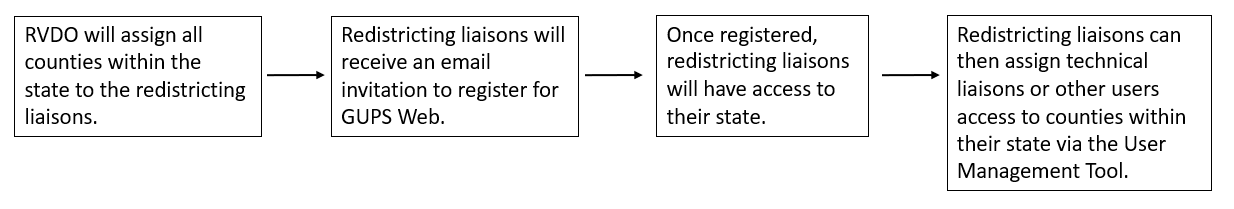
Figure 2: Workflow for Accessing GUPS Web
Ahead of the start of BBSP, all counties within a state will be assigned to the official redistricting liaison(s). The liaisons will then receive an email prompting them to create a GUPS Web account.
Once the GUPS Web account has been created by the official redistricting liaison, upon logging in to GUPS Web, the liaison(s) will be able to access all the counties within the state and assign work to technical liaisons and other stakeholders as described in section 3.2.4.
Once the GUPS Web account has been created, participants can navigate to the GUPS Web Login page <https://gupsweb.geo.census.gov/>, select the Login button. The participant will then be re-directed to another GUPS page where the participant will be prompted to enter their credentials--registered email and password--used to set up the account. After selecting Sign in, the participant will be logged into GUPS Web and directed to the GUPS Dashboard page; see section 3.2.
For BBSP, when a project is created, there is only one version of the project. It may be shared with other users by assigning them a user access role.
There are three access roles, each with different permissions, within the GUPS Web environment:
Project Owner
Project Collaborator
Project Viewer
Table 5: GUPS Web User Access Roles
User Role |
Assign/Revoke Access |
Edit Projects |
Delete Projects |
Submit to Census |
Read-Only Access |
Project Owner |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Project Collaborator |
|
X |
X |
X |
|
Project Viewer |
|
|
|
|
X |
Official redistricting liaisons will be automatically assigned the role of project owner for all counties in their state. As shown in Table 5, project owners can perform BBSP updates, delete projects, and submit projects to the Census Bureau. Additionally, project owners can assign project owner, project collaborator, and project viewer access roles to other participants. Project owners can also revoke a participant’s access at any time.
Even though the official redistricting liaison will automatically be assigned the project owner role by the RVDO at the start of BBSP, there can be multiple project owners for a county project. If a project owner assigns another participant (i.e., technical liaison) the project owner role, that new project owner now has all the same permissions as the official redistricting liaison.
Project collaborators are invited to projects by project owners and can make BBSP updates, submit projects to the Census Bureau, and delete projects to which they are assigned.
If a project owner wants a technical liaison to be able to make edits and submit to the Census Bureau without being able to assign or revoke access roles for other participants, the technical liaison should be assigned the project collaborator role.
If the project collaborator should not be able to submit projects to the Census Bureau, please let the project collaborator and RVDO know, so the office can ensure that submissions are coming from the appropriate participant. The RVDO will manually ensure submissions are only received from approved collaborators.
Project Viewers can only view data from specific projects assigned to them.
The GUPS Web Dashboard is the page displayed when participants log into GUPS Web. From the dashboard, participants can perform user management, view recent projects, and open projects. The dashboard button, see Figure 3, is displayed in GUPS Web no matter what actions the participant is performing, allowing participants to return to the dashboard.
![]()
Figure 3: GUPS Web Dashboard Button
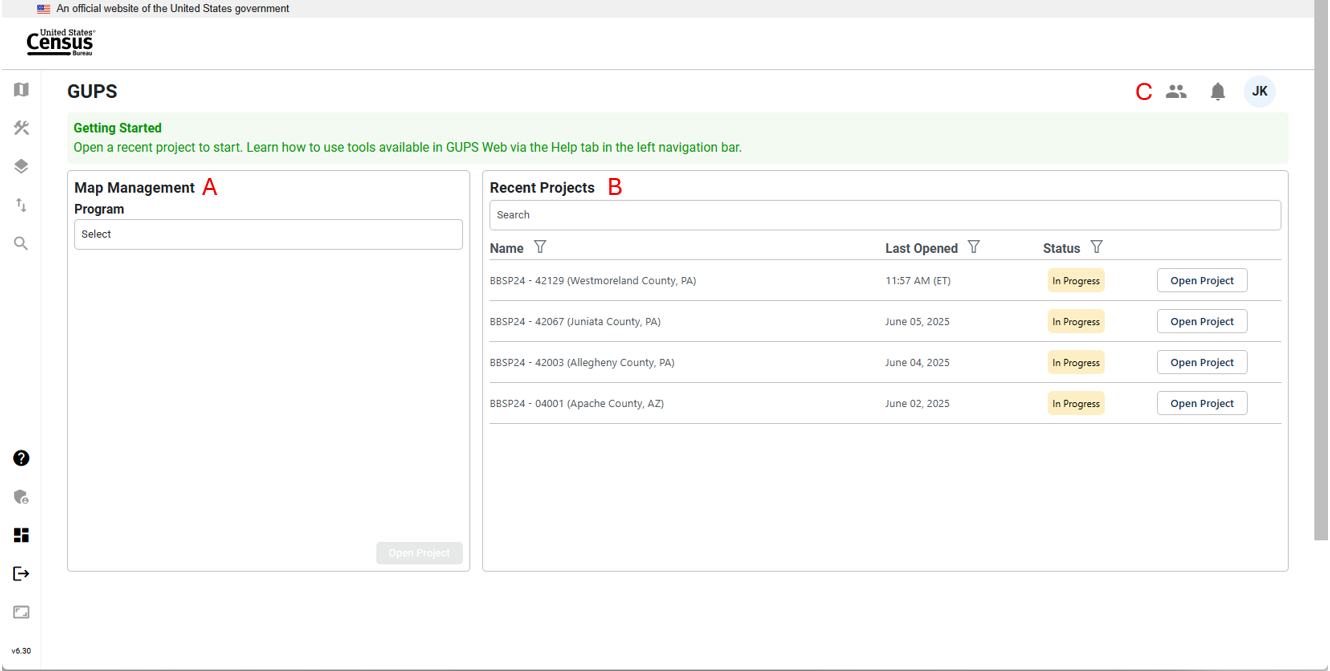
Figure 4: GUPS Web Dashboard Interface
Map Management, labeled as A in Figure 4, allows participants to open new or existing projects by selecting the state and then the county. If the participant does not have access to the project, they will not be able to open the project; see Figure 5. If an official redistricting liaison cannot access a county within their state, contact the RVDO at 301-763-4039 or at <rdo@census.gov>.
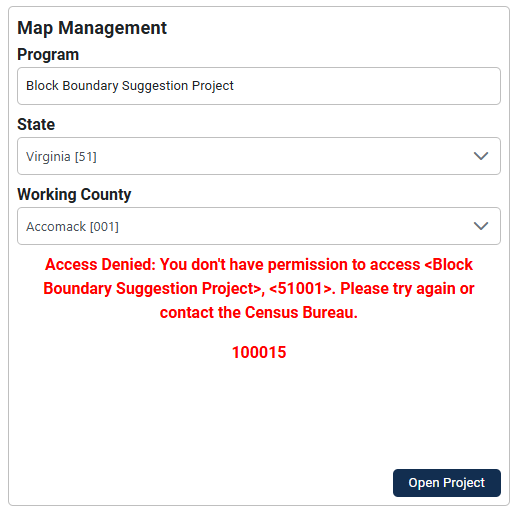
Figure 5: Example of Access Denied Message
Recent Projects, labeled as B in Figure 4, shows the participants a list of their 10 most recent projects, where they are assigned either project owner, project collaborator, or project viewer access. Additional information for the project is provided, including:
The last date/time the project was opened by any participant.
The status of the project:
New: No updates have been made in the project.
In Progress: Updates have been made:
Ready for Review: Project has been submitted to the Census Bureau.
The ability to open the project.
Once a project has been opened from the Map Management or Recent Projects interface, the project will display at the county level (for new projects) or at the last location saved from an earlier session. This is shown in Figure 6 and referred to as the map view in this document. The rest of Section 3 details the tools and actions that are available in the GUPS Web map view.
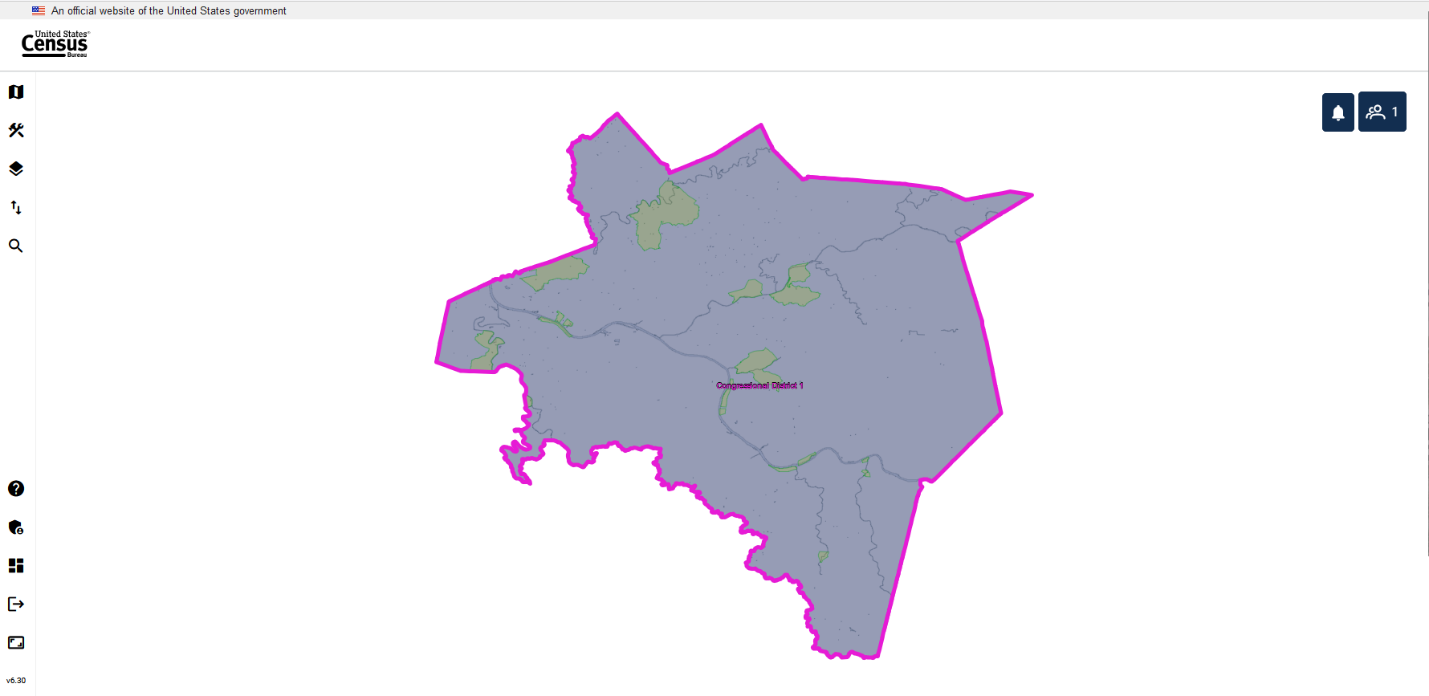
Figure 6: Example of a New Project Opened in GUPS Web (Map View)
At the start of BBSP, the RVDO will assign the project owner role to the official redistricting liaisons for all the counties in their state. It is up to the liaison to invite additional participants to GUPS Web as fellow project owners, project collaborators, or project viewers.
Only participants with a project owner access role can assign counties within their state to another project owner, project collaborator, or project viewer. The Invite Users interface is accessed by clicking on the User Management button, labeled as C in Figure 4 in the top right corner of the dashboard, and then selecting Invite Users from the dropdown. Participants must be invited to access the project.
![]()
Figure 7: User Management Module Button
Table 6: How to Invite a User to GUPS Web Project
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
To invite users, click on the User Management icon, see Figure 7, and select Invite Users. |
Step 2 |
Under Program on the left side of the screen, select Block Boundary Suggestion Project. |
Step 3 |
Select user role:
|
Step 4 |
In the personal message part of the screen, the user role will automatically be updated. |
Step 5 |
Select the State either by entering the FIPS Code (e.g., 42) or Name (e.g., Pennsylvania). |
Step 6 |
Once the state is selected, work can be assigned by selecting individual counties using the County ID/Name field or by checking the Select All box to select all the counties within the state that are currently assigned to the project owner. This prevents assigning counties that the project owner may not have access to. In the personal message section, the counties that are being assigned are populated automatically within the message. |
Step 7 |
Enter the email address for the invited participant in the Invite Users field. |
Step 8 |
Make any updates to the email text. |
Step 9 |
Click Invite to send or Cancel to cancel. |
Figure 8 shows an example where three (out of 67) counties were assigned to the new project owner. The current project owner was only assigned those three counties and selected Select All for the County ID/Name.
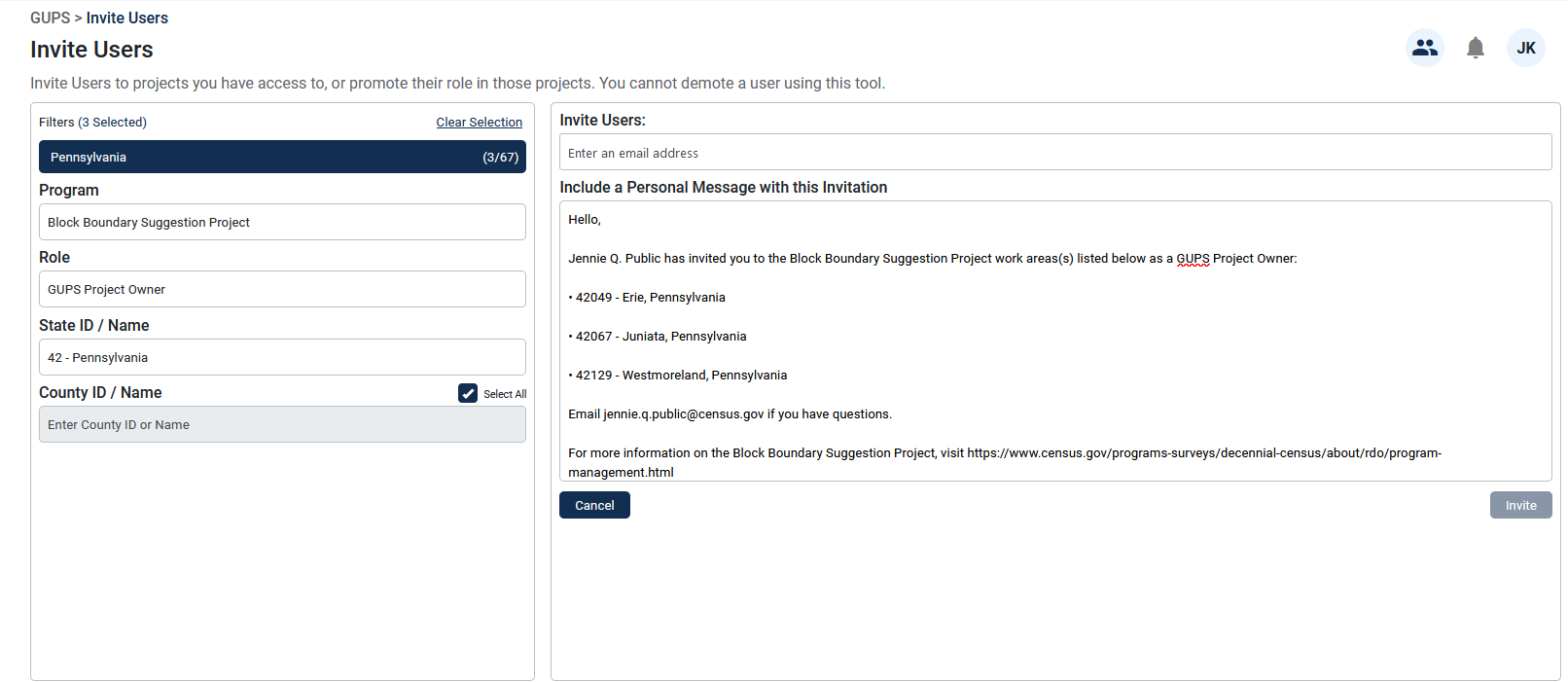
Figure 8: Invite Users Interface (County-Level)
Figure 9 shows an example where all 55 counties in state of West Virginia were assigned to a new project owner.
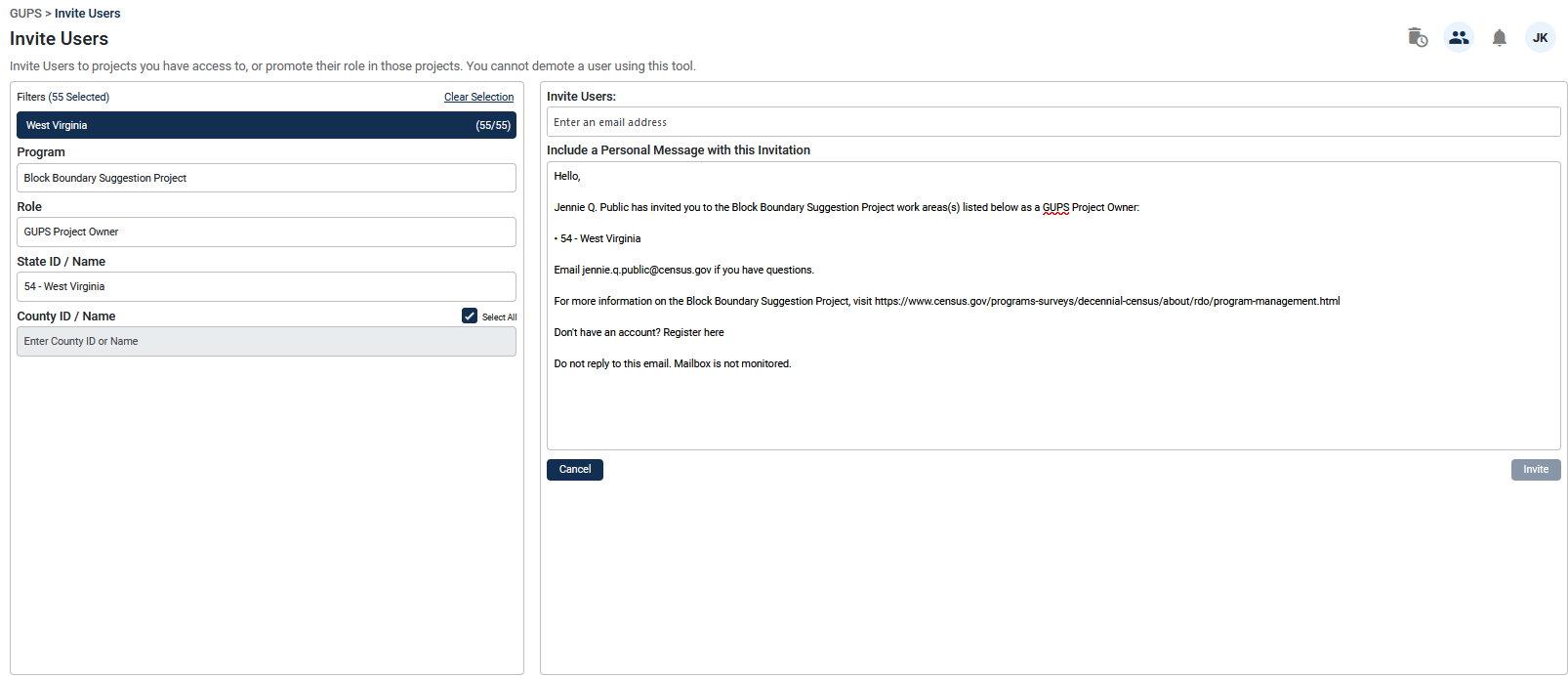
Figure 9: Invite Users Interface (State-Level)
The Manage Users Tool allows project owners to manage new or existing users based on their projects. The Manage Users interface is accessed through the User Management button labeled as C in Figure 4 in the top right corner of the dashboard and select Manage Users.
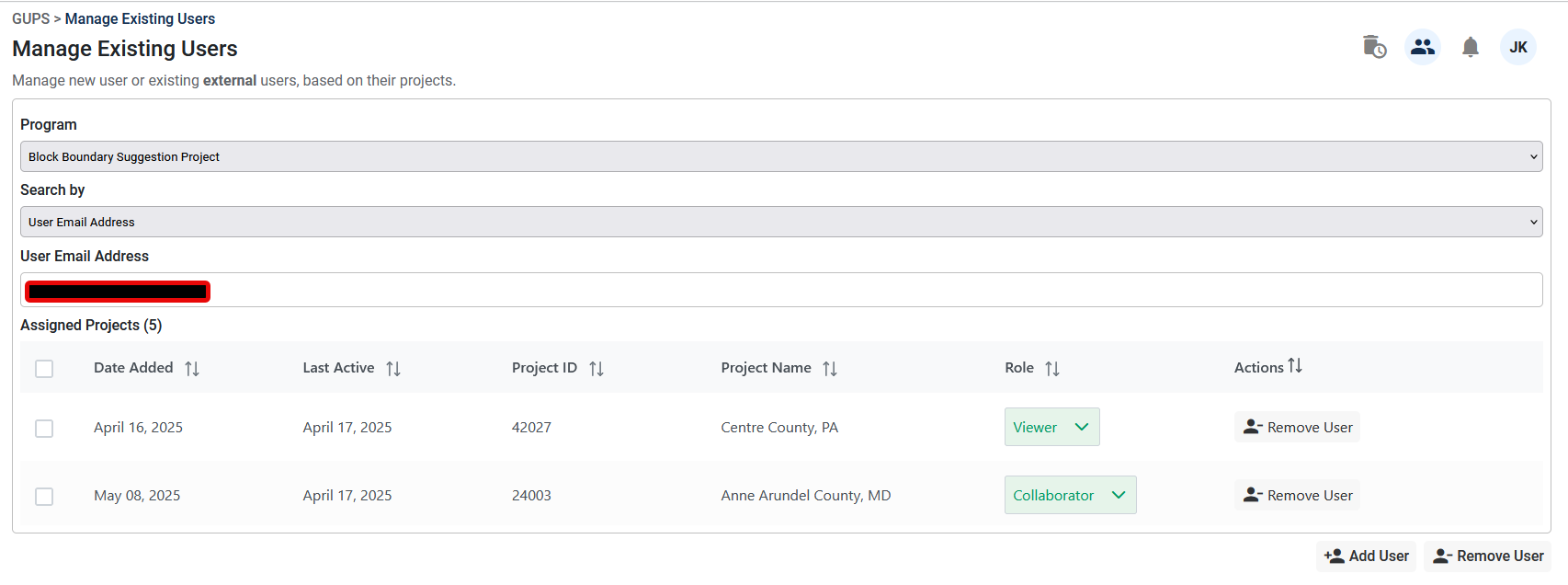
Figure 10: Manage Users Interface
Table 7: How to Utilize the Manage Users Interface
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
To manage users, click on the User Management button, see Figure 7, and select Manage Users. |
Step 2 |
Select Block Boundary Suggestion Project. |
Step 3 |
Select how to Search By:
Note: the example in Figure 10 was based on a user email address search. |
Step 4 |
Searching by State Code or Name, the following fields are displayed:
|
Step 5 |
Searching by user email address, the following fields are displayed:
|
Step 6 |
Below the Manage Users Interface, there is an “Add User” and “Remove User” button. These allow project owners to select multiple projects from the Interface to add or remove users from. |
This section describes the tools available in GUPS Web for project viewing and editing. All the tools are accessible from the dashboard, described in section 3.2, and in the map view as shown in Figure 11 with the tools identified.
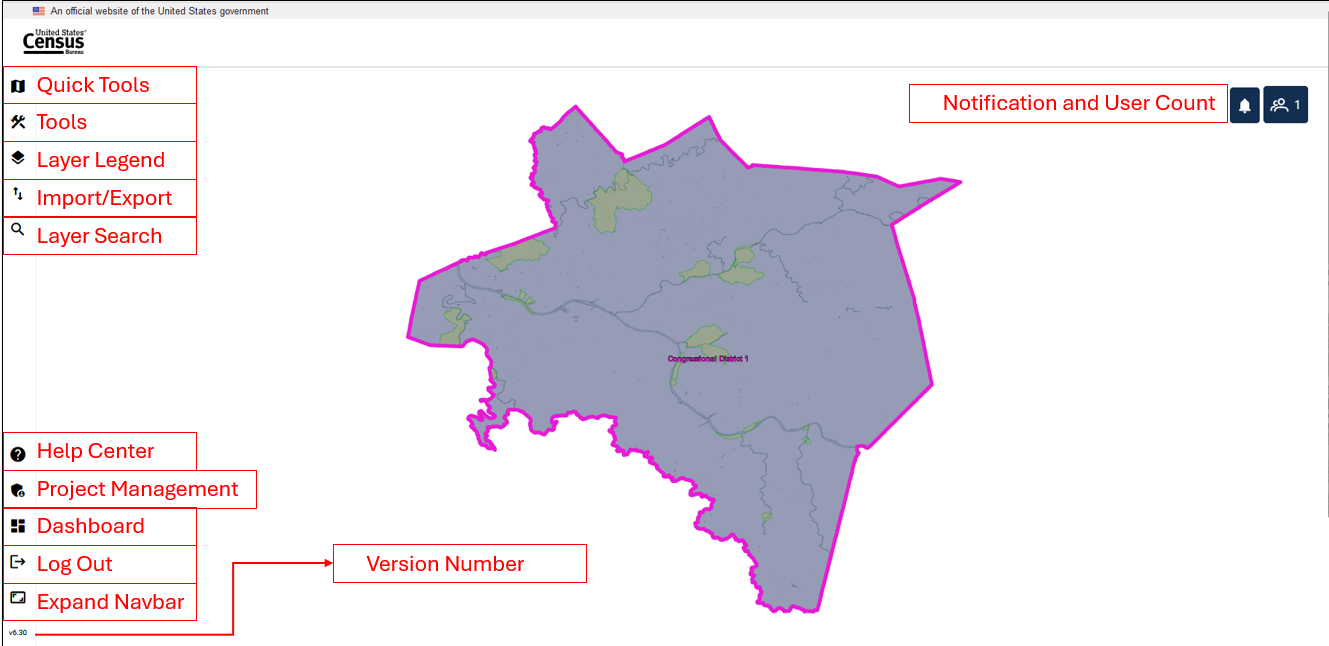
Figure 11: GUPS Web Map View with Tools Identified
On the left of the dashboard screen, there is the GUPS Web Navigation Bar (displayed vertically). The buttons are described below.
Table 8: GUPS Web Navigation Bar
Tool |
Icon |
Description |
Quick Tools |
|
Quick Tools are functions that are used often to navigate the map. The menu includes Pan, Zoom Last, Zoom Next, Add/Remove Esri Imagery, Zoom Full Extent, Zoom In, Zoom Out, and Save and Refresh. This tool is activated when a project is opened; see section 3.3.2. |
Tools |
|
Tools includes the View, Imagery, Selection, Edit, and Review Tools. This tool is activated when a project is opened; see section 3.3.3. |
Layer Legend |
|
Layer Legend depicts the layers in the map view. This tool is activated when a project is opened; see section 3.3.4. |
Import/Export |
|
Import/Export allows the user to import a reference shapefile, export a map as a pdf, jpg, or png, and submit to the Census Bureau for review. This tool is activated when a project is opened; see section 3.3.5. |
Layer Search |
|
This tool is not currently active for BBSP. Attribute tables can be used for search within the layers; see section 3.3.4.2. |
Help Center |
|
The Help Center is available for participants to obtain more information on GUPS Web, the supported programs, FAQs, and project tools. It is recommended to visit the BBSP Program Management Page for specific BBSP Guidance. <https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial-census/about/rdo/program-management.html>. |
Project Management |
|
The Project Management tool allows project owners and project collaborators to delete projects not intended for submission to the Census Bureau; see section 3.3.6. |
Dashboard |
|
Return to the GUPS Web Dashboard; see section 3.2. |
Log Out |
|
Log out of GUPS Web. |
Expand Navbar |
|
Expands the navigation toolbar which houses the tools described in this table. |
Version Number |
|
Note: For Quick Tools, Tools, Layer Legend, and Import/Export Tools clicking the button will expand the toolbar to show the tools and then clicking on the button again will collapse the tools.
The Quick Tools are functions that are used often to navigate the map. The menu includes the following actions:
![]()
Tool |
Icon |
Description |
Pan Map |
|
Shift the map in the map view without changing the map scale. |
Zoom Last |
|
Zoom the map view to the previous map extent. |
Zoom Next |
|
Zoom the map view forward to the next map extent. |
Add Esri Imagery |
|
Display satellite imagery on the map. |
Zoom Full |
|
Zoom the map view to the full extent of the county. |
Zoom In |
|
Display the map in the map view at a larger scale. |
Zoom Out |
|
Display the map in the window at a smaller scale. |
Save and Refresh |
|
Save current edits and refresh the map view. |
There are five sets of tools within GUPS Web to assist participants with performing their BBSP updates. These tools include View, Imagery, Selection, Edit, and Review. To access the tools, click on the Tools button shown in Figure 13. The navigation bar will expand to show the tools listed below.
![]()
View Tools includes the options to pan and zoom in and out of the map, identify features, measure distances, create bookmarks and add or remove a dynamic scale bar.
Click on the arrow next to View Tools to show the list of actions within the tool; see Figure 14.
The menu includes the following actions described in Table 10: View Tools.
Tool |
Description |
|
Shift the map in the map view without changing the map scale. |
|
Identify the selected geographic feature. |
|
Provide options to measure linear distance and area on the map. |
|
Zoom the map view to the full extent of the county. |
|
Zoom the map view to the rows selected in the attribute table. |
|
Zoom the map view to the extent of the active layer. |
|
View the current scale of the map view. |
|
Create, view, or delete bookmarks within the project. |
Figure 15: Imagery Tools Option
Imagery Tools provides the option of adding and removing Esri imagery or opening Google Maps or Bing Maps to view the selected location.
Click on the arrow next to Imagery Tools to show the list of actions within the tool; see Figure 15.
The menu includes the following actions described in Table 11.
Tool |
Description |
|
Display the selected map location in Google Maps after clicking on the map in a separate browser tab. |
|
Display the selected map location in Bing Maps after clicking on the map in a separate browser tab. |
|
Display satellite imagery in the map view. |
|
Remove satellite imagery from the map view. |

Figure 16: Selection Tools Option
Selection Tools allow the participant to select features in the active layer using a variety of selection types, including Select Features, Select by Polygon, and Select Freehand, as well as Deselect All.
Click on the arrow next to Selection Tools to show the list of actions within the tool; see Figure 16.
The menu includes the following actions described in Table 12.
Tool |
Description |
|
Left click on a single feature to select it or left click and drag to select multiple features. |
|
Draw a polygon around features to select them. |
|
Draw a freehand shape around features to select them. |
|
Clear the selected features. |
Edit Tools allow participants to make updates to their project. Edit tools are unique across participant programs.
Click on the arrow next to Edit Tools to show the list of actions within the tool; see Figure 17. The menu includes the following actions described in Table 13.
Tool |
Description |
|
Create and edit area landmarks and legal entities; see section 4.2 and section 4.3. |
|
Add a new linear feature; see section 4.1.1. |
|
Delete a linear feature or restore a deleted linear feature; see section 4.1.2 and 4.1.3. |
|
Split a linear feature from one segment to two segments; see section 4.1.5. |
|
Edit attributes of a selected linear feature; see section 4.1.4. |
|
Assign or remove a “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold” flag to a linear feature; see section 4.6. |
|
Add a 2030 linear feature extension to create a closed polygon for a suggested 2030 block; see section 4.6.5. |
|
Create a Block Area Grouping over water; see section 4.7.1. |
|
Delete a Block Area Grouping; see section 4.7.2 |
Figure 18: Review Tools Option
Review tools allow participants to perform different reviews for their updates within a project. Types of reviews are specific to participant programs.
Click on the arrow next to Review Tools to show the list of actions within the tool; see Figure 18.
The menu includes the following actions described in Table 14.
Tool |
Description |
|
Perform a systematic review of any area landmark or legal entity updates made in the project; see section 4.10. |
|
Perform a systematic review of linear features with block boundary suggestion flags sorted by BBSP category (Must Hold, Do Not Hold, NULL); see section 4.8. |
|
Perform a systematic review of 2020 linear feature extensions (if present) and take an action for 2030 (i.e., assign a “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold” flag or Ignore); see section 4.4.1. |
|
Perform a systematic review of small blocks (less than 3,000 square meters) that exist in the project based on the planned and suggested block boundaries; see section 4.9. |
The Layer Legend depicts the layers in the map view. It can be opened by clicking the Layer Legend button shown in Figure 19.
![]()
Figure 19: Layer Legend Button
Layers have been pre-styled and arranged for optimal use. The layers and their labels appear at varying scales depending on the layer. Layers can also be manually turned off and on depending on the geography that needs to be viewed. Use the arrows next to the layers to reveal or hide sub-layers for group layers.
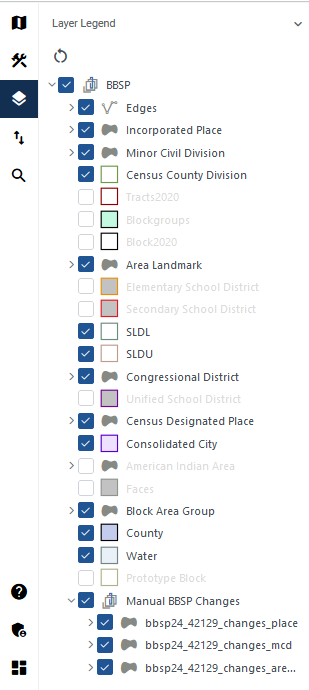
Figure 20: Layer Legend Interface
Note: For BBSP, the edges layer has an extensive sub-menu detailing the symbology showing planned and ineligible block boundaries as well as participant indicated “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags. It is not shown in this screenshot due to the size, but it is recommended to expand the edges sub-menu while making BBSP updates.
The order in which the layers appear determines the order that the layers display in the Map View. The layers at the top of the Layer Legend display on top of the layers that appear below them. To manage the order of layers, select and drag the layer to the desired position in the layer legend. Some layers may be blocked from view due to layers being drawn on top of them; this can be resolved by turning layers off and on.
Right-clicking on a layer reveals additional functions:
Open Attribute Table: Open an attribute table.
Zoom to Layer: Zoom to the full extent of the layer.
Zoom to Selection: Zoom to selected features.
Properties: Open layer properties.
Hide Labels: Hide and show labels.
Load Default Style: Revert to the default style (symbology).
Note: Participants may want to turn some layers off to better view their area of update if those layers are not relevant to the review.
At the bottom of the Layers Legend, there is a layer called “Manual BBSP Changes” and it includes three sub-layers; see Figure 20.
bbsp26_<ssccc>_changes_place (shows place changes)
bbsp26_<ssccc>_changes_mcd (shows MCD changes)
bbsp26_<ssccc>_changes_arealm (shows area landmark changes)
These layers are present in every project even if there are no changes for these geographies. When there are changes for these layers, participants can view the change polygons in the map view and the change attributes in the attribute table of the shapefiles listed above. These layers also populate the Boundary Review Interface; see section 4.10.
Attribute tables can be opened from the Layer Legend by selecting the layer, right clicking it, and selecting Open Attribute Table. Attribute tables in GUPS Web have built in functionality for sorting and filtering records. Participants can also select records within the attribute table and zoom to their location in the map view. Participants can choose to show all the records within the table, show all records that are currently visible in the map view, or show selected records.
Table 15: Attribute Table Tools
Tool |
Icon |
Description |
Show Features |
|
Choose which records in the attribute table to display: Show All, Show Features Visible on Map, or Show Selected Features. |
Filter |
|
Click on the Filter button to apply filters as described. |
Filter Options |
|
Once filter is selected, filter options allow the participant to tailor their filters for their search. |
Sort |
|
Sort the records within the column. |
Sort Ascending |
|
Indicates that the column is sorted in ascending order. |
Sort Descending |
|
Indicates that the column is sorted in descending order. |
Zoom to Selection |
|
Zoom to the selected feature(s) in the map view. |
Deselect All |
|
Clear all selected records. |
Clear Filters |
|
Clear applied filters and sorts. |
Table 16: How to Search the Attribute Table
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Open the attribute table from the Layer Legend. |
Step 2 |
Use the Filter or Sort functions to identify and view the feature(s). |
Step 2a |
To use the Filter option: Choose if the filter should “match all” records or “match any” records (this is only needed if there is more than one rule applied within the filter). Type in the search phrase. Then choose from the following: Starts With, Contains, Not Contains, Ends with, Equals, or Not Equals. Example: If the participant is searching for Ardmore Boulevard, they should click on the Filter button the FULLNAME column, leave the default Match All, select Starts With, and type in the search phrase of Ardmore. By using only Ardmore, the participant will find records that may include Blvd and Boulevard, but the participant would not find West Ardmore, as that starts with “West.” |
Step 4 |
To use the Sort option: Click on the Sort button. It will sort the features in ascending order (from A-Z). Click on the Sort button again to sort the features in descending order (from Z-A). Use Ctrl to sort on another field within the attribute table. |
Step 5 |
Once the results are shown within the table, select a single record and double click on the record to zoom to the feature. Select multiple records by holding down the shift key while clicking on all the records Use the Zoom to Selection tool to zoom to the extent that includes all the selected records. Use the Deselect All button clears the selected features. |
Step 6 |
Use the Clear Filters button to remove the filters. |
The Import/Export Tool, see Figure 21, allows the participant to import a reference shapefile, export a map as a pdf, jpg, or png, and submit the project to the Census Bureau for review.
Click on the arrow next to Import Tools or Export Tools to show the list of actions within the tool; see Figure 22.
![]()
Figure 21: Import/Export Button
Figure 22: Import/Export Interface
The menu includes the following actions described in Table 17.
Tool |
Description |
|
Import a shapefile to use as reference for the project. Importing a reference file does not create any updates in the project. |
|
Begin the submission to Census process. Located under Export Tools; see section 4.11.1.1. |
|
Download a copy of the project file. Located under Export Tools; see section 4.11.1.2. |
|
Export a map of the area displayed in the map view. Located under Export Tools; see section 4.11.1.3. |

Figure 23: Project Management Button
The Project Management Tool, see Figure 23, is a part of the GUPS Web Navigation Bar, described in section 3.3.1. This tool allows project owners and project collaborators to delete projects that they have access to; see Figure 24.
If a project was deleted and needs to be restored, please contact the RVDO at rdo@census.gov or 301-763-4039.

Figure 24: Delete Project Button
Note: Deleting projects will delete the project for all participants (project owners, project collaborators, and project viewers) who have access to the project and all edits that were made.
![]()
Figure 25: Notification Button
The notification button is in the top right of the map view; see Figure 25. Participants can click on the button to see if there are any notifications for participants. Notifications can include messages about scheduled and unscheduled downtimes or upcoming deadlines. Notifications can also be viewed on the dashboard when participants log in.

The user count button is in the top right of the map view; see Figure 26, It shows the current number of users in the project. If the participant clicks the icon, it will display the name(s) of the current user(s) in the project.
Section 4 details the process for making specific BBSP updates. The tools described in this section are within the Edit Tools menu in GUPS Web. Most of the sections describing updates will include an image of the button used to initiate the action, an image of the action (with certain aspects highlighted if applicable), and a table of steps.
Review the Census Bureau’s linear features (edges shapefile) to determine whether there are features that need to be added or deleted. Pay particular attention to any areas that have experienced population growth, and where there may be new housing or subdivisions not reflected in the Census Bureau’s geospatial data.
Refer to Table 1 for a complete list of MTFCCs for linear features.
The basic groupings of the MTFCCs are as follows:
S-class = Roads.
R-class = Railroads.*
P-class = Nonvisible Features.*
L-class, K-class, and C-class = Other Linear Features. *
H-class = Hydrography.*
The Census Bureau will also accept attribute updates (name and classification code) for MTFCCs in the S-class (roads). Added road features (except for highway ramps) require a feature name.
*These types of linear features should only be added if desired as a block boundary and therefore must have a “Must Hold” flag assigned to them when submitted to the Census Bureau.
Note: Please be aware that the Census Bureau will not process the wholesale spatial realignment of features merely to conform to an alternate spatial accuracy. If a feature is in the incorrect location in the Census Bureau’s feature network, mark the feature for deletion and then add it in the correct location. Take this action only if most of the realigned feature is more than 7.6 meters from the existing feature or interferes (is topologically incorrect) with relationships to other features.
![]()
Figure 27: Add Linear Feature Button
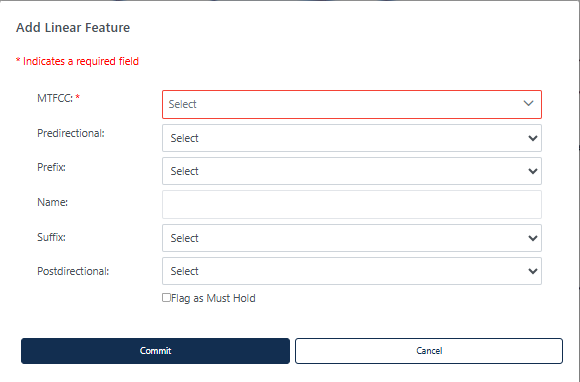
Figure 28: Add Linear Feature Dialog Window
Table 18: How to Add a Linear Feature
Note: When adding new linear features, imagery should be turned on within GUPS Web.
![]()
Figure 29: Delete/Restore Linear Feature Button
Table 19: How to Delete a Linear Feature
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select the Delete/Restore Linear Feature button; see Figure 29. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click on the linear feature to delete or left click and drag to select multiple features to delete at the same time. The edge(s) will be highlighted once selected. |
Step 3 |
Right click to delete the selected linear feature. If the linear feature selected for deletion has a “Must Hold” flag, a popup will appear “Warning: One or more of the linear features that you have selected for deletion has been flagged as a Must Hold. This action cannot be undone.” To continue with the deletion, click OK. To cancel the deletion, click Cancel. Figure 30 shows this popup. |
Step 4 |
An additional popup will appear reminding the participant that “Note that the features are marked for deletion in GUPS Web, however they may not be deleted from the MAF/TIGER System. If your goal is to ensure that the edge is not used as a block boundary, flag the edge(s) as a Do Not Hold.” This message can be turned off for the session by selecting “Do no show this message again.” Click Cancel to cancel the action or Click OK to continue with the delete action. Figure 31 shows this popup. |
Step 5 |
If the linear feature existed in the shapefiles, the deleted line appears with a red line symbology to show it has been marked for deletion. (Note: you may need to turn on the Deleted Linear Feature symbology from the Edges layer.) If the linear feature was newly added and then deleted, it is completely removed from the map view and cannot be restored. |
Note If the goal is to ensure that the edge is not used as a block boundary, refer to section Error! Reference source not found.Error! Reference source not found. on flagging the edges as “Do Not Hold” rather than using the delete function.
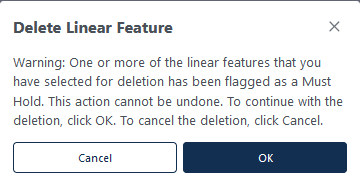
Figure 30: "Must Hold" Delete Warning
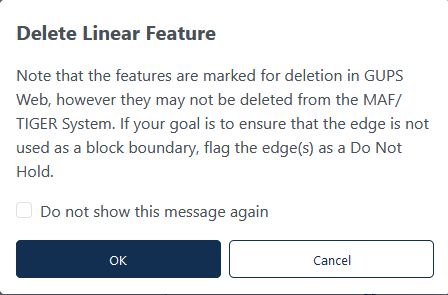
Figure 31: Delete Linear Feature Warning
Only existing linear features can be restored. Newly added linear features that were deleted cannot be restored.
Table 20: How to Restore a Deleted Linear Feature
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Delete/Restore Linear Feature button; see Figure 29. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click on the deleted linear feature to restore. |
Step 3 |
Right click to confirm the selected linear feature. |
Step 4 |
The red symbology will be removed from the linear feature. |
Note: If a linear feature was added and then deleted, it cannot be restored.
![]()
Figure 32: Modify Linear Feature Button
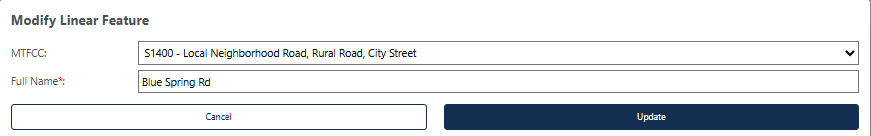
Figure 33: Modify Linear Feature Interface
Table 21: How to Modify a Linear Feature
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Linear Feature button; see Figure 32. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click on the linear feature to modify or left click and drag to select multiple features to modify at the same time. The edge(s) will be highlighted once selected. Selecting multiple edges is helpful if the linear feature is made up of several edges with the same Full Name and MTFCC. If the selected linear feature does not have matching Full Names and MTFCCs, they cannot be edited at the same time. |
Step 3 |
Right click to confirm the selected linear feature. |
Step 4 |
Update the MTFCC and/or Full Name; see Figure 33. If the linear feature is being modified from a road to a non-road feature, the Name will be removed from the feature. |
Step 5 |
Click Update to perform the modification or Cancel to cancel the modification. |
![]()
Figure 34: Split Linear Feature Button
Table 22: How to Split a Linear Feature
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Split Linear Feature button; see Figure 34. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click on the linear feature where the split should occur. There is no confirmation screen. |
Step 3 |
The linear feature has been split. |
The Census Bureau accepts updates to area landmarks (such as prison areas, state parks, and cemeteries) as part of the BBSP through the Modify Area Feature Tool. Allowable updates include:
Boundary corrections (adding and removing area).
Creating a new area landmark.
Removing an area landmark.
Changing or adding a name to an area landmark.
Changing/updating the MTFCC of an area landmark.
If the state plans to reallocate prisoners during redistricting, consider reviewing the existing area landmarks with MTFCCs K1235, K1236, K1237, and K1238, which represent areas with potential prison populations, or create new ones for those types of areas.
Updates to area landmarks and legal entities are made using the Modify Area Feature Tool.
![]()
Figure 35: Modify Area Feature Tool Button
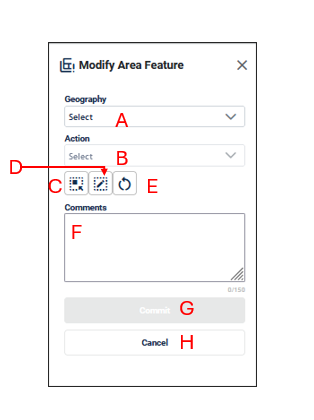
Figure 36: Modify Area Feature Interface
Geography (A) allows the participant to select the area features to create, delete or modify. These include Incorporated Places, Area Landmarks, and MCDs.
Action (B) allows the participant to select what action to perform on the area feature selected. The actions available will vary depending on the geography selected, but they include:
Annexation allows the participant to create annexations by adding area to the incorporated place or MCD. Documentation is required to process the update; see section 4.3.2.
Deannexation allows the participant to create deannexations by removing area from the place. Documentation is required to process the update; see section 4.3.3.
New: allows the participant to create a new area landmark (see section 4.2.4), incorporated place, and MCD. Documentation is required to process the insertion of new Incorporated Places or MCDs; see section 4.3.6.
Boundary Correction-Add Area allows the participant to create boundary corrections by adding area to the area landmark (see section 4.2.2), incorporated place or MCD; see section 4.3.4.
Boundary Correction-Remove Area: allows the participant to create boundary corrections by removing area from the area landmark (see section 4.2.3), incorporated place or MCD; see section 4.3.5.
Delete: allows the participant to delete an area landmark (see section 4.2.5) or incorporated place. Documentation is required to process the deletion for Incorporated Places or MCDs; see section 4.3.7.
Modify Attributes allows the participant to modify the attributes of an area landmark (see section 4.2.6Error! Reference source not found., incorporated place, or MCD see section 4.3.8.
Select Target Area Tool (C) allows the participant to select a geography to update using the map. It is helpful to use this tool when the geography is in the map view and the scale should remain the same.
Draw Polygon Tool (D) allows the participant to manually draw a boundary update.
Reset Polygon (E) allows the participant to remove the unsaved boundary update polygon.
Comments (F) allows the participant to include comments for specific actions. Comments are not required.
Commit (G) saves the update.
Cancel (H) cancels the update.
Note: When updating area landmarks, places, and MCDs participants do not need to digitize separate linear features to represent the boundaries of the area landmark. The change polygon that is drawn using the Draw Polygon Tool will represent the boundary and the Census Bureau will digitize the boundary edges accordingly.
![]()
Figure 37: Modify Area Feature Button
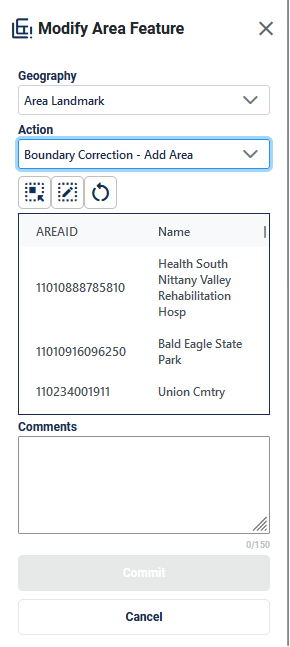
Figure 38: Modify Area Feature Tool Boundary Correction- Add Area Interface
Table 23: How to Add Area to an Area Landmark
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 38, select Area Landmark as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Boundary Correction - Add Area as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the area landmark record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the area landmark from the map to add area to. Note: when the selected area landmark is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to area landmark’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Once the area landmark is selected, use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the area that should be added to the area landmark. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 6 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 7 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
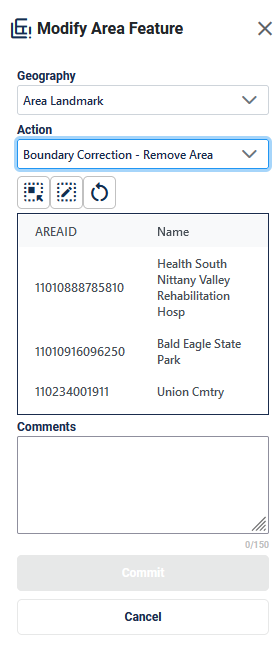
Figure 39: Modify Area Feature Tool Boundary Correction- Remove Area Interface
Table 24: How to Remove Area from an Area Landmark
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 39, select Area Landmark as the Geography |
Step 3 |
Select Boundary Correction - Remove Area as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the area landmark record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the area landmark from the map to remove area from. Note: when the selected area landmark is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to area landmark’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Once the area landmark is selected, use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the area that should be removed from the area landmark. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 6 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 7 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
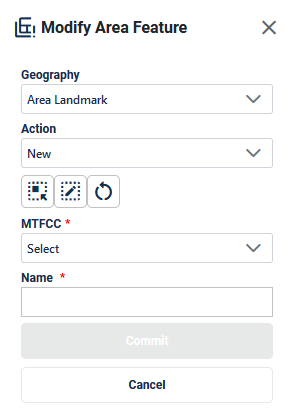
Figure 40: Modify Area Feature Tool New Area Landmark Interface
Table 25: How to Create a New Area Landmark
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 40, select Area Landmark as the Geography |
Step 3 |
Select New as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the boundaries of the new area landmark. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 5 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 6 |
Select the MTFCC Code. |
Step 7 |
Enter the Name. |
Step 8 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
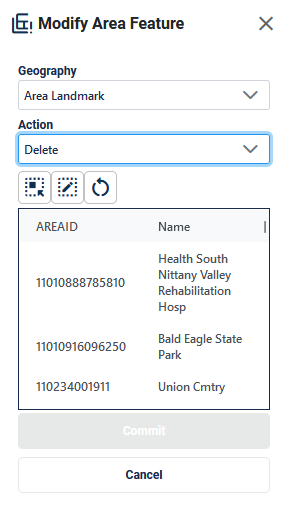
Figure 41: Modify Area Feature Tool Delete Area Landmark Interface
Table 26: How to Delete an Area Landmark
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 41, select Area Landmark as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Delete as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the area landmark record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the area landmark from the map to delete. |
Step 5 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
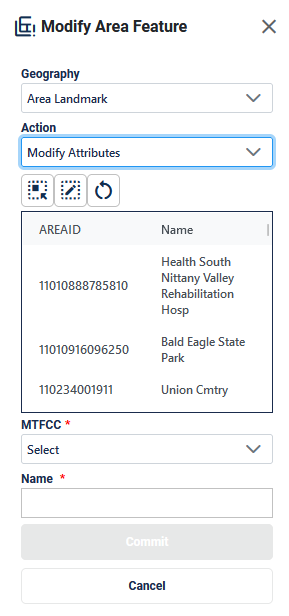
Figure 42: Modify Area Feature Tool Modify Attributes Interface
Table 27: How to Modify an Area Landmark
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 42, select Area Landmark as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Modify Attributes as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the area landmark record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the area landmark from the map to modify. |
Step 5 |
Edit the MTFCC and/or Name. |
Step 6 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |

Figure 43: Modify Area Feature Tool Modify Attributes Interface
Table 28: How to Modify an Area Landmark
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 42, select Area Landmark as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Modify Attributes as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the area landmark record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the area landmark from the map to modify. |
Step 5 |
Edit the MTFCC and/or Name. |
Step 6 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
Participants may provide legal boundary updates (annexations, deannexations, incorporations and disincorporations), along with their supporting documentation, or boundary corrections. The Census Bureau will assume the responsibility for reconciling the updates with the appropriate governments as part of the Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS).
Participants may submit legal boundary updates for MCDs and incorporated places. Although legal documentation (effective date, authority type, and documentation number) is not required for boundary updates submitted through the BBSP, the Census Bureau strongly encourages the submission of documentation to expedite our ability to reconcile and process any legal updates reported. Annexations and deannexations without supporting documentation should be submitted as boundary corrections. To report a new county, MCD, or incorporated place (without documentation) or to delete an existing MCD, incorporated place or county (without documentation), please call the RVDO at 301-763-4039, or email <rdo@census.gov>.
Note: The Census Bureau cannot guarantee these updates will be made, as we must adjudicate and receive concurrence for the updates from the official BAS contact.
When performing Annexations and Deannexations, the Modify Area Feature Tool will include the following fields in addition to the fields described in section 4.2.
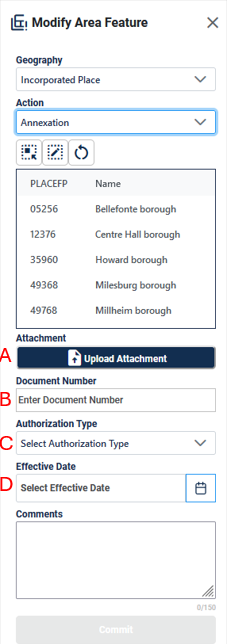
Figure 44: Modify Area Feature Tool Interface with Legal Fields
These fields include:
Attachment (A) allows the participant to upload the relevant documentation for the annexation, deannexation, new, or delete action.
Document Number (B) allows the participant to enter the ordinance or other legal documentation number authorizing the annexation, deannexation, new, or delete action.
Authorization Type (C) allows the participant to select the type of document that approved the annexation, deannexation, new, or delete action such as ordinance, resolution, or state law.
Effective Date (D) allows the participant to enter or select the date that the annexation, deannexation, new, or delete action becomes effective.
Note: When making changes to places and MCDs, participants do not need to digitize separate linear features to represent the boundaries of the area landmark. The change polygon that is drawn using the Draw Polygon Tool will represent the boundary and the Census Bureau will digitize the boundary edges accordingly.

Figure 45: Modify Area Feature Tool Annexation Interface
Table 29: How to Perform an Annexation
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 45, select Incorporated Place or MCD as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Annexation as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the Place/MCD record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the Place/MCD from the map to add area to. Note: when the selected Incorporated Place or MCD is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to Incorporated Place or MCD’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Once the Place/MCD is selected, use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the area that should be annexed. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 6 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 7 |
Upload an attachment of the document (optional) and enter the legal information into the Document Number, Authorization Type, and Effective Date fields to activate the commit button. If this documentation is unavailable, refer to section 4.3.4 and provide this as a Boundary Correction- Add Area. |
Step 8 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
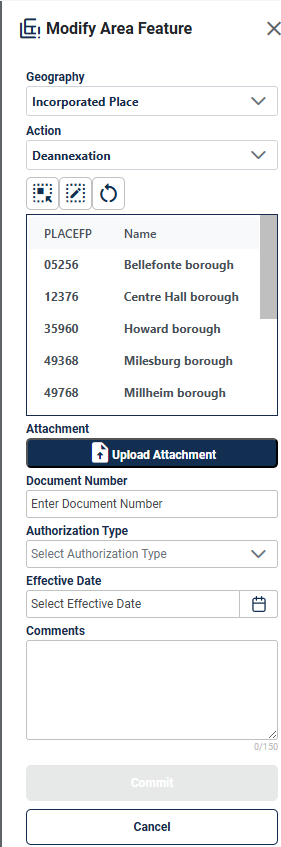
Figure 46:Modify Area Feature Tool Deannexation Interface
Table 30: How to Perform a Deannexation
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 46, select Incorporated Place as the Geography. This functionality is not available for MCDs. |
Step 3 |
Select Deannexation as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the Place record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the Place from the map to remove area from. Note: when the selected Incorporated Place is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to Incorporated Place’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Once the Place is selected, use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the area that should be deannexed. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 6 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 7 |
Upload an attachment of the document (optional) and enter the legal information into the Document Number, Authorization Type, and Effective Date fields to activate the commit button. If this documentation is unavailable, refer to section 4.3.5 and provide this as a Boundary Correction- Remove Area. |
Step 8 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
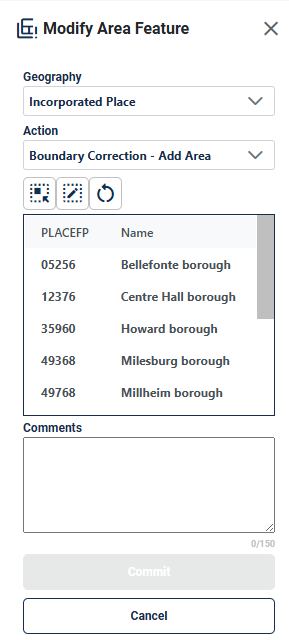
Figure 47: Modify Area Feature Legal Update Boundary Correction-Add Area Interface
Table 31: How to Add Area to a Incorporated Place or MCD
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 47, select Incorporated Place or MCD as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Boundary Correction - Add Area as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the Place/MCD record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the Place/MCD from the map to add area to. Note: when the selected Incorporated Place or MCD is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to Incorporated Place or MCD’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Once the Place/MCD is selected, use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the area that should be added. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 6 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 7 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
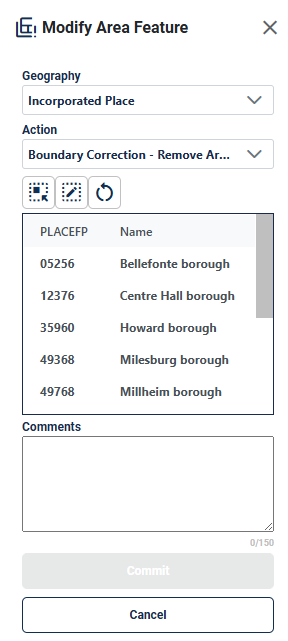
Figure 48:Modify Area Feature Legal Update Boundary Correction-Remove Area Interface
Table 32: How to Remove Area from an Incorporated Place
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 48, select Incorporated Place as the Geography. This functionality is not available for MCDs. |
Step 3 |
Select Boundary Correction - Remove Area as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the Place record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the Place/MCD from the map to add area to. Note: when the selected Incorporated Place is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to Incorporated Place’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Once the Place is selected, use the Draw Polygon Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting the area that should be removed. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 6 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 7 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
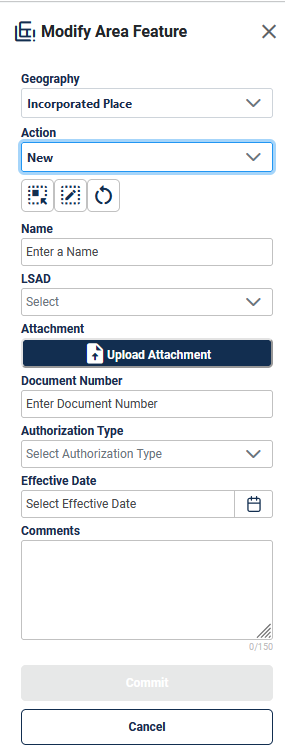
Figure 49: Add a New Legal Entity Interface
Table 33: How to Add a New Incorporated Place or MCD
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 49, select Incorporated Place or MCD as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select New as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Use the Draw Polygon Area Tool to manually draw a polygon reflecting boundaries of the new Place/MCD. Note these polygons will not automatically align with the linear features in the project. Please digitize them carefully to reflect the update but they do not need to exactly match. Start drawing with a single left or right click at starting point. GUPS Web will display a single blue point and line.
|
Step 5 |
To end drawing without saving, hold the shift key and left click or select the Reset Polygon Tool. |
Step 6 |
Enter the Name. |
Step 7 |
Select the Legal and Statistical Area Description (LSAD). |
Step 8 |
Upload an attachment of the document (optional) and enter the legal information into the Document Number, Authorization Type, and Effective Date fields to activate the commit button. If this documentation is unavailable, reach out to the RVDO at rdo@census.gov or 301-763-4039. |
Step 9 |
Click Commit or Cancel to cancel. |
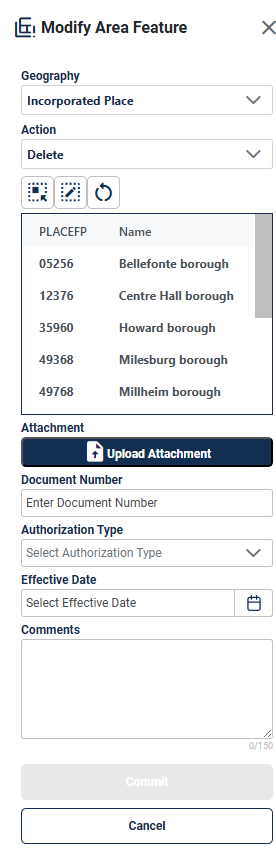
Figure 50: Delete a Legal Entity Interface
Table 34: How to Delete An Incorporated Place
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
On the Modify Area Feature Interface; see Figure 50, select Incorporated Place as the Geography. This functionality is not available for MCDs. |
Step 3 |
Select Delete as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the place record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the incorporated place from the map to delete. |
Step 5 |
Upload an attachment of the document (optional) and enter the legal information into the Document Number, Authorization Type, and Effective Date fields to activate the commit button. If this documentation is unavailable, reach out to the RVDO at rdo@census.gov or 301-763-4039. |
Step 6 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
Note: If the deleted incorporated place crosses a county boundary, it must be deleted in both counties separately. After making the change in the working county, return to Map Management, select the other county as the working county, and proceed to delete the entity in this county as well. If the deleted entity crosses more than one county boundary, complete the deletion in each county affected.

Figure 51: Modify Attributes of a Legal Entity Interface
Table 35: How to Modify the Attributes of an Incorporated Place or MCD
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Modify Area Feature button; see Figure 37. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Select Place or MCD as the Geography. |
Step 3 |
Select Modify Attributes as the Action. |
Step 4 |
Click on the Incorporated Place or MCD record from the list or use the Select Target Area Tool to select the Place/MCD from the map to add area to. Note: when the selected Incorporated Place or MCD is selected from the list and GUPS Web zooms to Incorporated Place’s full extent. Using the Select Target Area Tool will re-select the entity without zooming to the full extent. |
Step 5 |
Edit the Name, select the LSAD value, upload an attachment of any documentation available, enter the Document Number, select the authorization type, and add an Effective Date. If this documentation is unavailable, reach out to the RVDO at rdo@census.gov or 301-763-4039. |
Step 6 |
Click Commit to save or Cancel to cancel. |
All block boundary suggestions are contingent upon the lines intersecting to form a closed polygon at the time the Census Bureau creates blocks. As a result, all block boundary “Must Hold” suggestions, when combined with the features identified as planned holds, should form a closed polygon.
For the 2020 Census, BBSP participants could place a “Must Hold” flag on an existing feature that did not form a closed a polygon. To do this, the participant also added a feature extension to close the polygon and create a potential new block. Those 2020 feature extensions are included in the 2030 BBSP files for review and update. It is important to note that most counties do not have linear feature extensions to review.
The Census Bureau requests that participants review the 2020 linear feature extensions to determine if they are still needed. Please be aware that to hold an old 2020 feature extension as a 2030 block boundary, participants must take an action to again classify that extension as a “Must Hold” suggestion.
During the feature extension review, participants may:
Hold the old 2020 linear feature extension as a 2030 block boundary suggestion along with the feature from which the extension originates. If possible, when applying a Must Hold to a feature extension, review the extension against cadastral data or imagery to ensure it is in the most appropriate location.
Flag the old 2020 feature extension as a "Do Not Hold" as some linear features cannot be deleted from the MTS. Flagging the old 2020 linear feature extension as a "Do Not Hold" will help the Census Bureau ensure the feature extension no longer serves as a block boundary.
Ignore the 2020 linear feature extension. If no action is taken on a 2020 linear feature extension, the Census Bureau may delete the old extension or if kept, decide whether to hold the extension and the feature associated with it as a 2030 block boundary or not.
Some counties have linear feature extensions inserted in previous BBSP cycles. These extensions should be reviewed, and the edges should either be flagged as a “Must Hold”, “Do Not Hold”, or left as is.
Figure 52: Verify Linear Feature Extension Tool Button
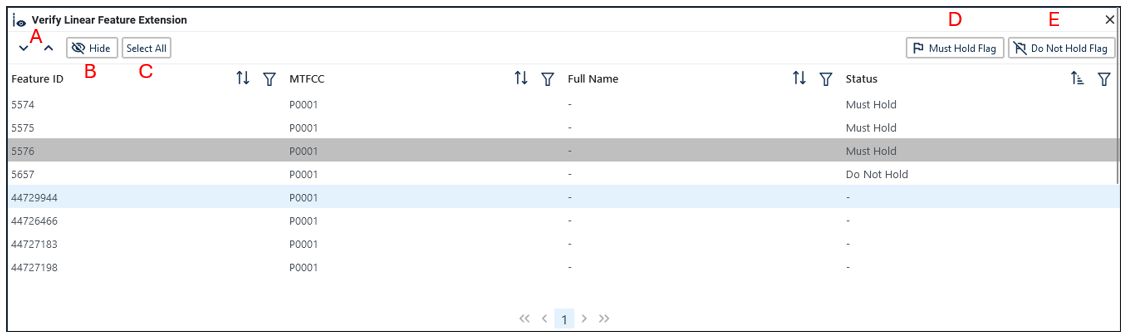
Figure 53: Verify Linear Feature Extension Tool Interface
Table 36: How to Review Linear Feature Extensions
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Open the Review Verify Linear Feature Extension Tool; see Figure 52. This is found under Review Tools described in section 3.3.3.5. |
Step 2 |
All 2020 linear feature extensions are displayed in the interface. Not all counties have linear feature extensions for review. |
Step 3 |
Click on a row to select the feature and zoom to it on the map. |
Step 4 |
There are several tools to sort through the Linear Feature Extension Review process; see Figure 53:
|
Step 5 |
Review that this edge has the appropriate block boundary flag assigned to it.
|
The prototype block shapefile shows what the planned 2030 blocks would look like if created using the geography as it exists at this time. The prototype block shapefile is a useful tool for participants to review their potential block geography and then use the “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags to make targeted updates.
Note: The prototype blocks are included in the Layer Legend (see section 3.3.4) and need to be turned on for review within the project.
In the prototype block shapefile, the Census Bureau assigned a block size indicator (BLKZIND field) to each block based on the range of the estimated number of housing units in the prototype block. These values can be used to identify both potentially small population blocks or large population blocks to split or merge using the “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags.
Note: Although discrete numbers have been established to assign each block a size value, the actual number of housing units in a block is approximate.
Block size indicators range from “A” through “I”, with “A” blocks having the most housing units and “I” having the least. Prototype blocks estimated to contain no housing units are assigned an indicator letter of “Z.”
Table 37: Block Size Indicator Values
Indicator |
Approximate Number of Housing Units |
A |
Greater than 2,000 |
B |
1,600-1,999 |
C |
1,200-1,599 |
D |
1,000-1,199 |
E |
700-999 |
F |
480-699 |
G |
400-479 |
H |
240-399 |
I |
1-239 |
Z |
Potential “0” housing unit block |
In the prototype block shapefile, the Census Bureau also calculated a shape index (SHAPEIDX) using a simple area to perimeter ratio method. The shape index value will be between 0 and 1. The closer the value to 1, the more compact the block. The closer the value to 0 the less compact the block. These values can be used to help identify less compact blocks to see if their shape would interfere with the ability to conduct redistricting (e.g. long sinuous water bodies). Then, the “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags can be used to remedy this if it is an issue.
BBSP participants can assign BBSP flags to features, suggest they be held or not held as block boundaries in the BBSP_2030 field of the edges shapefile. Using established criteria for delineating tabulation blocks, the Census Bureau has identified features already planned as 2030 block boundaries, which have a CBBFLG value of “4” in the edges shapefile. Refer to Table 1 for the complete planned feature list. The planned block boundaries may change if the criteria change, or if a feature’s attributes are updated through other Census programs.
The Census Bureau has also identified features that are ineligible to be 2030 block boundaries with a CBBFLG value of “9” in the edges shapefile. There are also features with no block boundary status assigned (CBBFLG value is null). Participants are not required to assign a BBSP flag (e.g., “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold”) to every feature in the file, nor should they.
Table 38: Description of Block Boundary Flagging Fields
Values |
Description |
BBSPFLG=1 |
2020 Participant Identified Must Hold Block Boundary |
BBSPFLG=2 |
2020 Participant Identified Do Not Hold Block Boundary |
BBSPFLG=4 |
2020 Census Identified Planned Block Boundary |
BBSPFLG=9 |
2020 Census Identified Ineligible Block Boundary |
BBSP_2030=1 |
2030 Participant Identified Must Hold Block Boundary (Will be null until set by participant) |
BBSP_2030=2 |
2030 Participant Identified Do Not Hold Block Boundary (Will be null until set by participant) |
CBBFLG=1 |
2030 Participant Identified Must Hold Block Boundary (Populated by Census Bureau during processing of BBSP submission. The field will be populated for BBSP Verification and future update cycles. Corresponds to value from the BBSP_2030 field.) |
CBBFLG=2 |
2030 Participant Identified Do Not Hold Block Boundary (Populated by Census Bureau during processing of BBSP submission. The field will be populated for BBSP Verification and future update cycles. Corresponds to value from the BBSP_2030 field.) |
CBBFLG=4 |
2030 Census Identified Planned Block Boundary |
CBBFLG=9 |
2030 Census Identified Ineligible Block Boundary |
All BBSP participant-provided 2030 Census “Must Holds,” i.e., BBSP_2030 = 1, combined with existing features and other planned block boundaries, must form closed polygons.
2030 Census planned block boundaries, i.e., CBBFLG = 4, are an indication of what the Census Bureau plans to use as a 2030 Census block boundary if they were defined today. The planned block boundaries may change if the criteria changes, or if the feature attributes are updated through other Census programs.
BBSP participant-provided 2030 Census “Do Not Hold” flag(s), i.e., BBSP_2030 = 2, will not be honored if the line they are placed on needs to be held for other purposes. For example, if a “Do Not Hold” flag was placed on an incorporated place boundary, the “Do Not Hold” flag would not be honored.
Table 39: Block Boundary Flagging Symbology
Value |
Symbology |
Description |
Planned Block Boundaries CBBFLG=4 |
|
Edges that are planned block boundaries have a blue halo symbology. |
Ineligible Block Boundaries CBBFLG=9 |
|
Edges that are ineligible block boundaries have a red halo symbology. |
“Must Hold” BBSP_2030=1 |
|
Edges that are flagged as a “Must Hold” that are neither planned nor ineligible block boundaries have a dark blue line. |
“Do Not Hold” BBSP_2030=2 |
|
Edges that are flagged as a “Do Not Hold” that are neither planned nor ineligible block boundaries have a dark red line. |
“Must Hold” on a Planned Block Boundary CBBFLG=4 BBSP_2030=1 |
|
Edges that are planned block boundaries and have been flagged as a “Must Hold” have the dark blue line representing the “Must Hold” with the lighter blue planned block boundary line visible. |
“Do Not Hold“ on a Planned Block Boundary CBBFLG=4 BBSP_2030=2 |
|
Edges that are planned block boundaries and have been flagged as a “Do Not Hold” have the dark red line representing the “Do Not Hold” with the lighter blue planned block boundary line visible. |
“Must Hold” on an Ineligible Block Boundary CBBFLG=9 BBSP_2030=1 |
|
Edges that are ineligible block boundaries and have been flagged as a “Must Hold” have the dark blue line representing the “Must Hold” with the lighter red ineligible block boundary line visible. |
“Do Not Hold” on an Ineligible Block Boundary CBBFLG=9 BBSP_2030=2 |
|
Edges that are ineligible block boundaries and have been flagged as a “Do Not Hold” have the dark red line representing the “Do Not Hold” with the lighter red ineligible block boundary line visible. |
NULL |
|
Edges that have no block boundary flags vary between roads and invisible edges (dark brown) and hydro features (blue). |
CD/SLD Block Split CBBFLG=S |
|
For Reference Only: Edges that have been flagged as a CD/SLD Block Split have a green/gray halo symbology. |
Participants may assign a “Must Hold” flag to features to suggest them as 2030 block boundaries. Candidates for assigning a “Must Hold” flag are:
Newly added features.
Features not currently planned as block boundaries.
To ensure features planned as 2030 block boundaries are held should the Census Bureau change their “planned” status.
Participants may wish to assign a “Must Hold” flag to features that are planned 2030 block boundaries in case the block definition criteria or feature classification codes change between when BBSP occurs and when the Census Bureau creates the 2030 Census blocks. Assigning a “Must Hold” to a planned block boundary feature will increase the likelihood that the feature will become a 2030 block boundary.
Be aware that assigning a “Must Hold” flag to a feature that is ineligible to be a block boundary or assigning a “Do Not Hold” flag to a feature that is planned to be a 2030 block boundary does not ensure that the Census Bureau will honor the request. The Census Bureau will re-evaluate the feature’s status based on the participant’s suggestion.
All “Must Hold” flags are contingent upon the features intersecting to form a closed polygon at the time the Census Bureau creates the 2030 blocks.
To hold a feature as a 2030 block boundary when the feature does not form a closed polygon, add a feature extension to close the polygon. Feature extensions must meet the following criteria:
Extensions, combined with other features and planned holds, must form a closed polygon.
Extensions must be no longer than 300 feet. (If an extension needs to be longer than 300 feet, participants must provide justification.)
Extensions must be a straight line originating from the end of a road feature.
Extensions must terminate on a non-road feature, except for highways (i.e., extensions may terminate on highways – MTFCC S1100).
![]()
Figure 54: Feature Flagging Tool Button
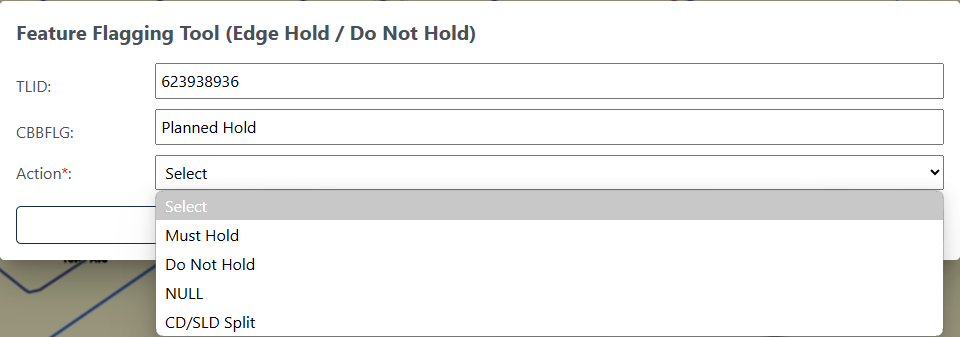
Figure 55: Feature Flagging Tool Interface
Table 40: How to Apply a "Must Hold" Flag
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click the Feature Flagging Tool button; see Figure 54. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click on the linear feature or left click and drag to select multiple linear features. |
Step 3 |
Right click to start editing. |
Step 4 |
The Feature Flagging Tool Interface opens; see Figure 55. Select the Action (flag) to apply to the linear feature: Must Hold. |
Step 5 |
Click on Update to save or Cancel to cancel. The symbology will update. |
Note: If the participant is performing boundary corrections, annexations, or deannexations to legal entities, do not flag the new boundaries with a “Must Hold” flag. The BAS team may adjudicate the updates with the BAS contact and apply the updates in a different manner than how they were submitted. However, the new legal boundaries will automatically be held as 2030 block boundaries.
“Do Not Hold” Flags
Participants may assign “Do Not Hold” flags to features that they do not want to become 2030 block boundaries. Potential candidates for assigning a “Do Not Hold” flag may include:
Private roads, trails, and unimproved roads.
Hydrographic features with no area, shown as a single-line feature, such as streams or creeks.
Any feature creating unnecessary blocks, such as highway ramps, traffic circles, or cul-de-sacs shown as open circles or “lollipops” in the Census geospatial files, and similar features.
Be aware that assigning a “Do Not Hold” flag to a feature that is a 2030 planned block boundary may not be honored if that boundary is needed to meet other Census criteria or program needs. For example, if a “Do Not Hold” flag is placed on an incorporated place boundary, the “Do Not Hold” will not be honored.
Table 41: How to Apply a "Do Not Hold" Flag
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click the Feature Flagging Tool button; see Figure 54. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click on the linear feature or left click and drag to select multiple linear features. |
Step 3 |
Right click to start editing. |
Step 4 |
The Feature Flagging Tool Interface opens; see Figure 55. Select the Action (flag) to apply to the linear feature: Do Not Hold. |
Step 5 |
Click on Update to save or Cancel to cancel. The symbology will update. |
Note: If the participant is performing boundary corrections, annexations, or deannexations to legal entities, do not flag the previous boundaries with “Do Not Hold” flags. The BAS team may adjudicate the updates with the BAS contact and apply the updates in a different manner than how they were submitted.
Table 42: How to Remove a "Must Hold" or "Do Not Hold" Flag
Note: Figure 55 shows CD/SLD Split as an option for in the Feature Flagging Tool. This should only be applied when creating block splits during Phase 4 Collection of Post-2020 Census Congressional and State Legislative District Plans and is not part of the BBSP update process.
To hold a feature as a 2030 block boundary when the feature does not form a closed polygon, add a feature extension to close the polygon.
![]()
Figure 56: Add Linear Feature Extension Button
Table 43: How to Add a Linear Feature Extension
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Select Add Linear Feature Extension button; see Figure 56. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 2 |
Left click |
Step 3 |
To digitize the linear feature extension, left-click on the location where the linear feature ends to draw the linear feature extension and right-click to end the extension.
|
Step 4 |
If the linear feature extension is over 300 feet long, a justification for the length must be entered. |
Step 5 |
The linear feature extension will be shown and automatically flagged with a “Must Hold” flag. |
During the 2030 Census block creation, the Census Bureau will automatically group islands to form a single block if they have no road features and the islands fall within a 5-kilometer radius. Participants may also choose to group specific islands to create a single 2030 Census block, called a Block Area Grouping (BAG). The criteria for creating a BAG are as follows:
BAG must consist of two or more islands.
BAG perimeter must be entirely over water.
BAGs cannot overlap.
BAGs cannot cross the boundary of other geographies, such as county or incorporated place boundaries.
BAG delineation is optional, and most appropriate for states with hydrographic areas that contain many islands.
Figure 57: Create Block Area Grouping Button
Table 44: How to Create a Block Area Grouping
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Turn on the Block Area Grouping layer in the Layer Legend. |
Step 2 |
Select Create Block Area Grouping button; see Figure 57. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 3 |
Digitize the BAG polygon by left clicking to begin drawing the BAG and continue to left click at each vertex (shape point) of the line. Press 'd' to delete previous vertices. |
Step 4 |
Left click on the starting point of the BAG to close the BAG. |
Step 5 |
Right click to complete the polygon. It will turn blue when it is completed. |
Step 6 |
The Block Area Grouping confirmation dialog box opens and click OK to save the BAG or Cancel to cancel the action. |
![]()
Figure 58: Delete Block Area Grouping Button
Table 45: How to Delete a Block Area Grouping
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Turn on the Block Area Grouping layer in the Layer Legend. |
Step 2 |
Select the Delete Block Area Grouping button; see Figure 58. This is found under Edit Tools described in section 3.3.3.4. |
Step 3 |
Left click on the BAG to delete. |
Step 4 |
Right click to complete the selection. |
Step 5 |
The Block Area Grouping confirmation dialog box opens and click OK to delete the BAG or Cancel to cancel the action. |
The Block Boundary Review Tool allows participants to systematically navigate to features on the map by 2030 “Must Hold” and “Do Not Hold” flags for review and further update if desired. Block boundary suggestions must be reviewed at least once before submitting updates to the Census Bureau.
![]()
Figure 59: Block Boundary Review Button
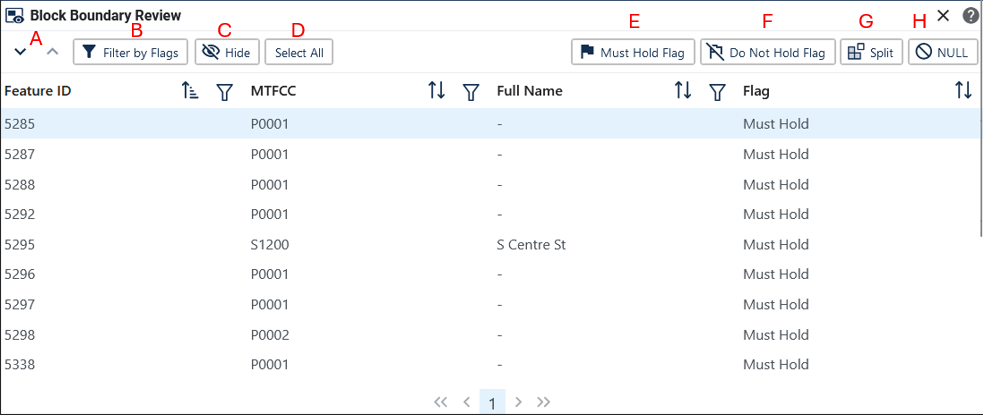
Figure 60: Block Boundary Review Interface
Table 46: How to Review Block Boundary Flags
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click on the Block Boundary Review button; see Figure 59. This is found under Review Tools described in section 3.3.3.5. |
Step 2 |
All block boundary updates are displayed in the Block Boundary Review Table. |
Step 3 |
Click on a row to select the feature and zoom to it on the map. |
Step 4 |
There are several tools to sort through the Block Boundary Review table; see Figure 60:
|
Step 5 |
Review that this edge has the appropriate block boundary flag assigned to it.
|
Step 6 |
Note: Split flags are assigned during Phase 4 - Collection of the Post 2020 Census Congressional and State Legislative Plans. This option should not be added or removed during the BBSP update process.
The Potential Small Block Check reviews the edges within the project and returns a list of potential small blocks that exist in the project based on the planned and suggested block boundaries.
All small blocks under 3,000 square meters are identified and listed. Within this list of potential small blocks:
Type “ - “: Small blocks under 3,000 square meters that are created by the planned block boundaries and do not include “Must Hold” flags.
Type A: Small blocks of 500 square meters or less that have one or more bounding edges where a "Must Hold" flag is involved.
Type B: Small blocks of 500.1 square meters to 3,000 square meters that have one or more bounding edges where a "Must Hold" flag is involved.
If the small blocks are unwanted or unintentional, they can be adjusted through Block Boundary Suggestion Flagging (i.e., remove the “Must Hold” flag from a bounding edge or apply a “Do Not Hold” flag). Potential small blocks must be reviewed at least once before submitting updates to the Census Bureau.
![]()
Figure 61: Potential Small Block Check Button

Figure 62: Potential Small Block Check Interface
Table 47: How to Review Potential Small Block Output
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click on the Potential Small Block Check button; see Figure 61. This is found under Review Tools described in section 3.3.3.5. |
Step 2 |
Click on a row to select the feature and zoom to it on the map. Filter and sort are available. |
Step 3 |
If potential small blocks can be adjusted by applying or removing “Must Hold” or “Do Not Hold” flags, the participant should open the Feature Flagging Tool (under Edit Tools; see section 4.6) and apply the correct flags. |
Step 4 |
It is recommended to run the check several times while editing the project. |
The Boundary Review Tool allows updates to area landmarks and legal entities (Incorporated Places and MCDs) to be viewed. Records can be clicked on to navigate from update to update. In addition, legal information can be added via the Boundary Review interface.

Figure 63: Boundary Review Button
Figure 64: Boundary Review Selection Interface
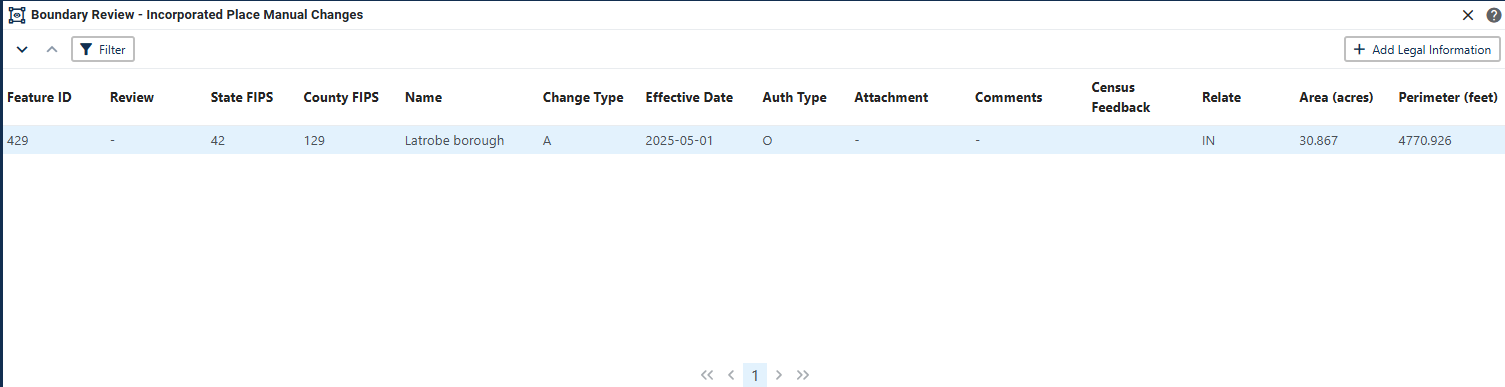
Figure 65: Boundary Review Tool Interface
Table 48: How to Review Boundary Changes
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click on the Boundary Review button; see Figure 63. This is found under Review Tools described in section 3.3.3.5. |
Step 2 |
Select which layer to view; see Figure 64. Only layers with changes will be available to select. |
Step 3 |
Click on a row to select the feature and zoom to it on the map. |
Step 4 |
If spatial edits need to be made use Modify Area Feature Tool (see section 4.2 and 4.3Error! Reference source not found. to apply the edits. Legal Information can be updated by clicking on the Add Legal Information button within the Review table. |
The Census Bureau conducts the RDP activities through the official liaison appointed by the governor and legislative leadership of the state. The official liaisons are responsible for making BBSP updates and submitting the projects to the Census Bureau. However, the official liaisons have two options for designating technical liaisons to assist them in making BBSP updates on behalf of the state.
• Option 1. Official liaisons can formally designate technical liaisons who are able to perform geographic updates and submit completed updates to the Census Bureau on their behalf. Official liaisons should reach out to the RVDO at 301-763-4039 or <rdo@census.gov> to make technical liaison designations.
• Option 2. Official liaisons can delegate work to designees who perform the updates and submit the updates back to the official liaison. The official liaison will submit the work to the Census Bureau if they approve the work. If the official liaison determines that BBSP work completed by a designee requires changes or additional work, it is the official liaison's responsibility to decide whether to make the changes or return the project to their designee for further updates.
The liaison responsible for submitting updates to the Census Bureau should submit completed, county-level files on a flow basis to the Census Bureau directly through GUPS Web. Do not hold files to submit all at once. Submit files as they are completed, especially at the beginning of the update period, so that the Census Bureau can provide feedback if there are errors, omissions, or other concerns.
Projects can be directly submitted to the Census Bureau from GUPS Web, bypassing the Secure Web Incoming Module (SWIM). Project owners and collaborators can submit projects.
![]()
Figure 66: Import/Export Button
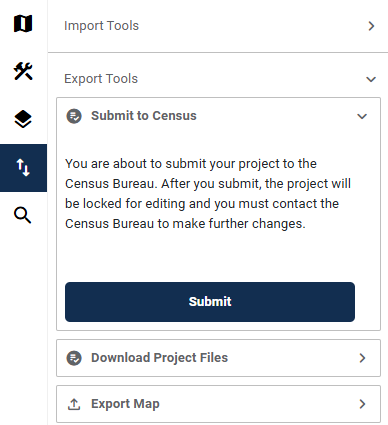
Figure 67: Submit to Census Interface
Table 49: How to Submit a Project to Census
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
While in the project that should be submitted, click the Import/Export button on the GUPS Web Navigation Bar; see Figure 66. |
Step 2 |
Expand Export Tools and then select Submit to Census; see Figure 67. |
Step 3 |
Select Submit. |
Step 4 |
The project has been submitted to the Census Bureau. If the project needs to be recalled, reach out to the RVDO at 301-763-4039 OR rdo@census.gov. |
Note: Please alert the RVDO to any technical liaisons (project owners and project collaborators) who are approved to submit projects to the Census Bureau to ensure the correct submission processing.
This allows users to download a copy of the current project submission for their records.
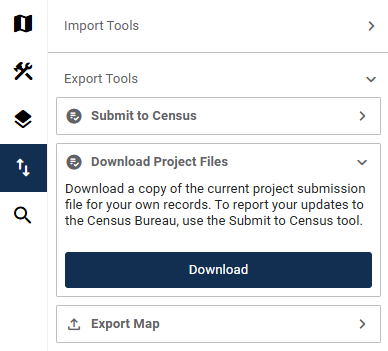
Figure 68: Download Project Files Interface
Table 50: How to Download Project Files
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click the Import/Export button on the GUPS Web Navigation Bar; see Figure 66. |
Step 2 |
Expand Export Tools and then select Download Project Files; see Figure 68. |
Step 3 |
Select Download. |
Step 4 |
Click Confirm to continue the download or Cancel to cancel. |
This allows participants to export a map (in pdf, png, or jpeg form) of a specific area.
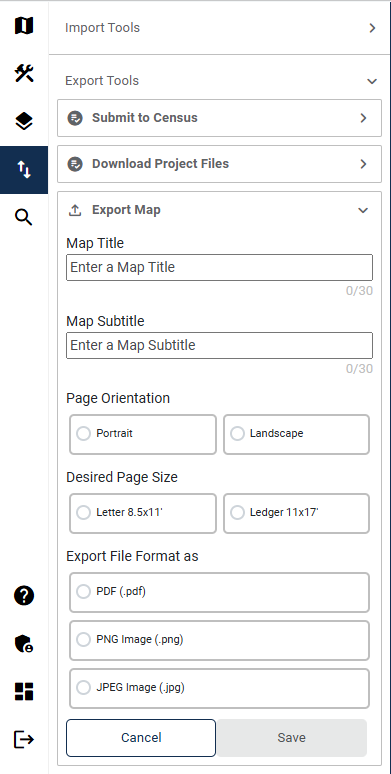
Figure 69: Export Map Interface
Step |
Description |
Step 1 |
Click the Import/Export button on the GUPS Web Navigation Bar; see Figure 66. |
Step 2 |
Expand Export Tools and then select Export Map; see Figure 69. |
Step 3 |
Enter following fields:
Select the following fields:
|
Step 4 |
Click Save to export the map or Cancel to cancel. |
Partnership Shapefiles reflect the legal boundaries and names for all governments, as reported through the previous year’s BAS. Participants can access the partnership shapefiles from two locations:
Download the partnership shapefiles from the Geography Partnership website at:
<www.census.gov/geographies/mapping-files/time-series/geo/partnership.html>
Download the partnership shapefiles from the FTP site at:
<https://www2.census.gov/geo/pvs/>
Census Bureau files are in GCS NAD83 format and can be projected into any local coordinate system/project. Most GIS software packages will allow users to transform file coordinate systems and projections.
State Level Shapefile Names – PVS_25_v2_<layername>_<SS>.shp where <SS> is the number corresponding to the state, for example, “24” and <shpname> is the abbreviation for the geography type represented in the shapefile.
Table 52: State Shapefile Names
Shapefile Layer |
<layername> |
Alaska Native Regional Corporation |
anrc |
American Indian / Alaska Native Areas – Statistical |
aias |
American Indian Areas – Legal |
aial |
American Indian Areas 2020 – Legal |
aial2020 |
American Indian Tribal Subdivisions – Legal |
aitsl |
American Indian Tribal Subdivisions – Statistical |
aitss |
Congressional Districts |
cd |
Core Based Statistical Areas |
cbsa |
Hawaiian Home Lands |
hhl |
School Districts (Elementary) |
elsd |
School Districts (Secondary) |
scsd |
School Districts (Unified) |
unsd |
School Districts Administrative Areas |
sdadm |
State Legislative Districts (Upper / Senate) |
sldu |
State Legislative Districts (Lower / House) |
sldl |
Public Use Microdata Areas 2020 |
puma2020 |
2020 Census Tracts |
tracts2020 |
Census Designated Places |
cdp |
Counties and Equivalent Areas |
county |
Counties and Equivalent Areas 2020 |
county2020 |
County Subdivisions – Legal |
mcd |
Incorporated Places |
place |
States and Equivalent Areas |
state |
Tribal Block Groups |
tbg |
Tribal Census Tracts |
tct |
Urban Areas Census 2020 |
uac |
Block Area Grouping |
bag |
County Level Shapefile Names – PVS_25_v2_<layername>_<SSCCC>.shp, where <SSCCC> is the number corresponding to the state and county, for example, “24001” and <shpname> is the abbreviation for the geography type represented in the shapefile.
Table 53: County Shapefile Names
Shapefile Layer |
<layername> |
Alaska Native Regional Corporation |
anrc |
American Indian / Alaska Native Areas – Statistical |
aias |
American Indian Areas – Legal |
aial |
American Indian Tribal Subdivisions – Legal |
aitsl |
American Indian Tribal Subdivisions – Statistical |
aitss |
Congressional Districts |
cd |
Core Based Statistical Areas |
cbsa |
Hawaiian Home Lands |
hhl |
School Districts (Elementary) |
elsd |
School Districts (Secondary) |
scsd |
School Districts (Unified) |
unsd |
School Districts Administrative Areas |
sdadm |
State Legislative Districts (Upper / Senate) |
sldu |
State Legislative Districts (Lower / House) |
sldl |
Public Use Microdata Areas 2020 |
puma2020 |
Urban Growth Areas |
uga |
Census Block Groups |
bg |
Census Blocks – Current |
tabblock |
Census Blocks – 2020 Census |
tabblock2020 |
Census Tracts – Current |
curtracts |
2020 Census Tracts |
tracts2020 |
Census Designated Places |
cdp |
Consolidated Cities |
concity |
Counties and Equivalent Areas |
county |
County Subdivisions for counties with Legal Subdivisions |
mcd |
County Subdivisions for counties with Legal Subdivisions |
ccd |
Incorporated Places |
places |
Subbarios |
submcd |
Tribal Block Groups |
tbg |
Tribal Census Tracts |
tct |
Urban Areas 2020 Census |
uac |
All Lines |
edges |
Area Landmarks |
arealm |
Hydrography – Area |
water |
Point Landmarks |
pointlm |
Geographic Offsets |
offset |
Block Area Grouping |
bag |
Face Geometry with all geocodes |
faces |
The tables in this section show the shapefile layouts for the county-level partnership shapefiles that are in the GUPS Web Layer Legend.
Table 54: All Lines (Edges) Shapefile (PVS_25_v2_edges)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
TLID |
10,0 |
Number |
Permanent Edge ID |
TFIDL |
10,0 |
Number |
Permanent Face ID, Left |
TFIDR |
10,0 |
Number |
Permanent Face ID, Right |
MTFCC |
5 |
Char |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FIDELITY |
1 |
Char |
Indication to a respondent when their entity boundary has changed through spatial enhancement |
FULLNAME |
40 |
Char |
Decoded Feature Name with abbreviated qualifier, direction, and feature type |
SMID |
22,0 |
Number |
Spatial Tmeta ID |
SMIDTYPE |
1 |
VARCHAR2 |
Source attribution for boundary edges. PLSS, Parcels, Surveyed, etc. |
RTTYP |
1 |
VARCHAR2 |
Route type code |
BBSPFLG |
1 |
Char |
Indicates the Redistricting Data Project participant's submitted request of an EDGE for selection for holding. |
CBBFLG |
1 |
Char |
Indicates the status of an EDGE for a selection as tabulation block boundary |
BBSP_2030 |
1 |
Char |
New BBSP Flag |
CHNG_TYPE |
4 |
Char |
Type of area update |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
LTOADD |
10 |
Char |
Left to address |
RTOADD |
10 |
Char |
Right to address |
LFROMADD |
10 |
Char |
Left from address |
RFROMADD |
10 |
Char |
Right from address |
ZIPL |
5 |
Char |
Left from ZIP Code |
ZIPR |
5 |
Char |
Right from ZIP Code |
EXTTYP |
1 |
Char |
Extension type |
MTUPDATE |
10 |
date |
Date of last update to the edge |
Table 55: Area Landmark Shapefile (PVS_25_v2_arealm)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
String |
State code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
String |
County code |
MTFCC |
5 |
String |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FULLNAME |
120 |
String |
Complete name associated with the area landmark |
AREAID |
22 |
String |
Landmark identification number, or Object ID |
ANSICODE |
8 |
String |
American National Standards Institute feature code for the county or equivalent area feature code for the area landmark |
PARTFLG |
1 |
String |
Part flag indicator, indicates if only part of a feature is represented |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
String |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
10 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
String |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
String |
Justification |
BAG |
3 |
String |
Block area grouping |
Table 56: Block Area Grouping Shapefile (PVS_25_v2_bag)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
NEW_CODE |
6 |
Char |
New Census BAG Code |
BAGCE |
3 |
Char |
Block Area Grouping |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 57: Census Blocks- 2020 (PVS_25_v2_tabblock2020)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP20 |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP20 |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
TRACTCE20 |
6 |
Char |
Census Tract Code |
BLOCKCE |
4 |
Char |
Tabulation block number |
BLOCKID20 |
15 |
Char |
FIPS State Code, FIPS County Code, Census Tract Code, Tabulation Block Number |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
HOUSING20 |
9,0 |
Number |
2020 Housing |
POP20 |
9,0 |
Number |
2020 Population Count |
Table 58: Congressional Districts (PVS_25_v2_cd)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
CDFP |
2 |
Char |
Congressional District Code |
CDTYP |
1 |
Char |
Congressional District Type |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
NEW_CODE |
2 |
Char |
New Congressional District Code |
RELTYPE1 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type1 |
RELTYPE2 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type2 |
RELTYPE3 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type3 |
RELTYPE4 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type4 |
RELTYPE5 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type5 |
REL_ENT1 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity1 |
REL_ENT2 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity2 |
REL_ENT3 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity3 |
REL_ENT4 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity4 |
REL_ENT5 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity5 |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
CDSESSN |
3 |
Char |
Congressional District Session Code |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char
|
Vintage
|
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
Table 59: Counties and Equivalent Areas (PVS_25_v2_county)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
BASID |
11 |
Char |
11-digit Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) ID |
COUNTYNS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI feature code for county or equivalent feature |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
Char |
Authorization type for legal area updates |
DOCU |
120 |
Char |
Supporting documentation |
AREA |
10,3 |
Number |
Acreage of area update |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 60: Minor Civil Divisions (PVS_25_v2_mcd)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
COUSUBFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 County Subdivision code |
BASID |
11 |
Char |
11-digit Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) ID |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
COUSUBNS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI feature code for the county subdivision |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
Char |
Authorization type for legal area updates |
DOCU |
120 |
Char |
Supporting documentation |
AREA |
10,3 |
Number |
Acreage of area update |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 61: Faces (PVS_25_v2_faces)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
TFID |
20 |
Number |
Permanent Face ID |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
TRIBSUBCE |
3 |
Char |
Census Tribal Subdivision Code |
TTRACTCE |
6 |
Char |
Tribal Census tract Code |
TBLKGRPCE |
1 |
Char |
Tribal Census Block Group Code |
AIANNHCE |
4 |
Char |
Current Census AIANNH code |
AIANNHCE20 |
4 |
Char |
2020 Census AIANNH code |
COMPTYP |
1 |
Char |
Indicates if reservation (or equivalent) or off-reservation trust land is present |
ANRCFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS ANRC Code |
SLDUST |
3 |
Char |
SLD Upper Chamber Code |
SLDLST |
3 |
Char |
SLD Lower Chamber Code |
ELSD |
5 |
Char |
Current ELSD Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
SCSD |
5 |
Char |
Current SCSD Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
UNSD |
5 |
Char |
Current UNSD Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
SDADM |
5 |
Char |
Current SDADM Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
CDFP |
2 |
Char |
Congressional District Code |
TRACTCE |
6 |
Char |
Census Tract Code |
UACE |
5 |
Char |
Census Urban Area Code |
CBSAFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS CBSA Code |
BLKGRPCE |
1 |
Char |
Census Block Group Code |
BLOCKCE |
4 |
Char |
Tabulation block number |
SUFFIX1CE |
2 |
Char |
Census Block Suffix 1 |
SUFFIX2CE |
2 |
Char |
Census Block Suffix 2 |
BAGCE |
3 |
Char |
Block Area Grouping |
PUMACE20 |
5 |
Char |
Public Use Microdata Area Code 2020 |
SUBMCDFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 Sub-Minor Civil Division Code |
UGACE |
5 |
Char |
Urban Growth Area code |
STATEFP20 |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP20 |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
TRACTCE20 |
6 |
Char |
Census Tract Code |
PLACEFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 Place Code |
COUSUBFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 County Subdivision code |
CONCITYFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 Place Code |
CDSESSN |
3 |
Char |
Congressional District Session Code |
LWFLG |
1 |
Char |
Land/Water Flag |
Table 62: Water (PVS_25_v2_water)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
ANSICODE |
8 |
Char |
Represents the official code for use by Federal agencies for data transfer and dissemination. |
MTFCC |
5 |
Char |
MAF/TIGER Feature Class Code |
FULLNAME |
120 |
Char |
Prefix Direction Code, Prefix Type code, Base Name, Suffix Type Code, Suffix Direction code |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
HYDROID |
22 |
Char |
Object ID |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
Table 63: Incorporated Place (PVS_25_v2_place)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
PLACEFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 Place Code |
BASID |
11 |
Char |
11-digit Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) ID |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
PLACENS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI feature code for the place |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
Char |
Authorization type for legal area updates |
DOCU |
120 |
Char |
Supporting documentation |
AREA |
10,3 |
Number |
Acreage of area update |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 64: State Legislative Districts (Upper/Senate) (PVS_25_v2_sldu)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
SLDUST |
3 |
Char |
SLD Upper Chamber Code |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
NEW_NAME |
100 |
Char |
New SLDU name |
NEW_CODE |
3 |
Char |
New SLDU code |
RELTYPE1 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type1 |
RELTYPE2 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type2 |
RELTYPE3 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type3 |
RELTYPE4 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type4 |
RELTYPE5 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type5 |
REL_ENT1 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity1 |
REL_ENT2 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity2 |
REL_ENT3 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity3 |
REL_ENT4 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity4 |
REL_ENT5 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity5 |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
LSY |
4 |
Char |
Legislative Session Year |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
Table 65: State Legislative Districts (Lower/House) (PVS_25_v2_sldl)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
SLDLST |
3 |
Char |
SLD Lower Chamber Code |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
NEW_NAME |
100 |
Char |
New SLDL name |
NEW_CODE |
3 |
Char |
New SLDL code |
RELTYPE1 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type1 |
RELTYPE2 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type2 |
RELTYPE3 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type3 |
RELTYPE4 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type4 |
RELTYPE5 |
2 |
Char |
Relationship Type5 |
REL_ENT1 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity1 |
REL_ENT2 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity2 |
REL_ENT3 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity3 |
REL_ENT4 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity4 |
REL_ENT5 |
8 |
Char |
Relationship Entity5 |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
LSY |
4 |
Char |
Legislative Session Year |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
Table 66: American Indian/Alaska Native Areas (PVS_25_v2_aial)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
BASID |
11 |
Char |
11-digit Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) ID |
AIANNHCE |
4 |
Char |
Census AIANNH code |
COMPTYP |
1 |
Char |
Indicates if reservation (or equivalent) or off-reservation trust land is present, or both |
AIANNHFSR |
1 |
Char |
Flag indicating level of recognition of an American Indian, Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian tribe or group |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
AIANNHNS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI numeric identifier for AIANNH Areas |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
Char |
Authorization type for legal area updates |
DOCU |
120 |
Char |
Supporting documentation |
AREA |
10,3 |
Number |
Acreage of area update |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 67: School Districts - Elementary (PVS_25_v2_elsd)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
SDLEA |
5 |
Char |
Current ELSD Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
LOGRADE |
2 |
Char |
Low grade |
HIGRADE |
2 |
Char |
High grade |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
SDTYP |
1 |
Char |
Census School District Type |
POLYID |
4 |
Char |
Record ID for each ELSD Update polygon for linking to the Submission Log |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 68: School Districts- Secondary (PVS_25_v2_scsd)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
SDLEA |
5 |
Char |
Current SCSD Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
LOGRADE |
2 |
Char |
Low grade |
HIGRADE |
2 |
Char |
High grade |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
SDTYP |
1 |
Char |
Census School District Type |
POLYID |
4 |
Char |
Record ID for each SCSD update polygon for linking the Submission Log |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 69: School Districts- Unified (PVS_25_v2_unsd)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
SDLEA |
5 |
Char |
Current UNSD Local Education Agency (LEA) Code |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
LOGRADE |
2 |
Char |
Low grade |
HIGRADE |
2 |
Char |
High grade |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
SDTYP |
1 |
Char |
Census School District Type |
POLYID |
4 |
Char |
Record ID for each UNSD update polygon for linking to the Submission Log |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 70: Census Block Groups (PVS_25_v2_bg)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
TRACTCE |
6 |
Char |
Census Tract Code |
BLKGRPCE |
1 |
Char |
Block Group Code |
BLKGRPID |
12 |
Char |
FIPS State code, FIPS County Code, Census Tract Code, Block Group Code |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
BGTYP |
1 |
Char |
Block Group Characteristic Flag |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 71: Census Tracts- 2020 (PVS_25_v2_tracts2020)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
TRACTCE |
6 |
Char |
Census Tract Code |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Base Name portion of the Standardized Name |
TRACTID |
11 |
Char |
FIPS State Code, FIPS County Code, Census Tract Code |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
TRACTTYP |
1 |
Char |
Tract Characteristic Flag |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification
|
TRACTLABEL |
7 |
Char |
Tract number used for LUCA geocoding |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
POP20 |
9,0 |
Number |
2020 Population |
Table 72: Census Designated Places (PVS_25_v2_cdp)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS County Code |
PLACEFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 Place Code |
PLACENS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI feature code for the place |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
PARTFLG |
1 |
Char |
Part flag indicator |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 73: Consolidated Cities (PVS_25_v2_concity)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
CONCITYFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 Place Code |
BASID |
11 |
Char |
11-digit Boundary and Annexation Survey (BAS) ID |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
PLACENS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI feature code for the place |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of area update |
EFF_DATE |
8 |
Date |
Effective date or vintage |
AUTHTYPE |
1 |
Char |
Authorization type for legal area updates |
DOCU |
120 |
Char |
Supporting documentation |
AREA |
10,3 |
Number |
Acreage of area update |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
Table 74: Census County Divisions (PVS_25_v2_ccd)
Attribute Field |
Length |
Type |
Description |
STATEFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS State Code |
COUNTYFP |
3 |
Char |
FIPS county code |
COUSUBFP |
5 |
Char |
FIPS 55 County Subdivision code |
NAMELSAD |
100 |
Char |
Name with translated LSAD |
COUSUBNS |
8 |
Char |
ANSI feature code for the county subdivision |
LSAD |
2 |
Char |
Legal/Statistical Area Description |
FUNCSTAT |
1 |
Char |
Functional Status |
CLASSFP |
2 |
Char |
FIPS 55 class code describing an entity |
CHNG_TYPE |
2 |
Char |
Type of point update |
RELATE |
120 |
Char |
Relationship description |
JUSTIFY |
150 |
Char |
Justification |
NAME |
100 |
Char |
Name |
VINTAGE |
2 |
Char |
Vintage |
The MTFCC is a 5-digit code assigned by the Census Bureau to classify and describe geographic objects or features. A full list of MTFCC codes and descriptions can be found at <www.census.gov/library/reference/code-lists/mt-feature-class-codes.html

| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 0000-00-00 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy