1545-0074 Supporting Statement
1545-0074 Supporting Statement.docx
U.S. Individual Income Tax Return
OMB: 1545-0074
SUPPORTING STATEMENT
Internal Revenue Service
U.S. Individual Income Tax Returns and Related Forms,
Schedules, Attachments, and Published Guidance
OMB Control Number 1545-0074
CIRCUMSTANCES NECESSITATING COLLECTION OF INFORMATION
Sections 6011 & 6012 of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) require individuals to prepare and file income tax returns annually. These forms and related schedules are used by individuals to report their income subject to tax and compute their correct tax liability.
Regulations section 1.6011-1 explains that every person subject to any tax, or required to collect any tax, under Subtitle A of the Code, shall make such returns or statements as are required by the regulations. The return or statement shall include therein the information required by the applicable regulations or forms. Section 1.6012-1 explains the general guidelines for individuals required to make returns of income.
Copies of the prescribed return forms are so far as possible furnished to taxpayers by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). A taxpayer will not be excused from making a return, however, by the fact that no return form has been furnished to him. Taxpayers not supplied with the proper forms should make application therefor to the district director in ample time to have their returns prepared, verified, and filed on or before the due date with the internal revenue office where such returns are required to be filed. Each taxpayer should carefully prepare his return and set forth fully and clearly the information required to be included therein. Returns which have not been so prepared will not be accepted as meeting the requirements of the Code. In the absence of a prescribed form, a statement made by a taxpayer disclosing his gross income and the deductions there from may be accepted as a tentative return, and, if filed within the prescribed time, the statement so made will relieve the taxpayer from liability for the addition to tax imposed for the delinquent filing of the return, provided that without unnecessary delay such a tentative return is supplemented by a return made on the proper form.
OMB clearance for the burden estimate will be requested before the relevant tax filing season but after the IRS has had the opportunity to update its models with prior year data and to make necessary revisions to draft forms (including providing drafts to public for comment) and is sought on an annual basis instead of on the regular 3-year Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA) cycle. Doing so ensures that new and updated forms can be made available for use on a timelier basis.
This information collection request (ICR) covers the actual reporting, recordkeeping, and third-party disclosure burden associated with the forms and their associated schedules listed in Appendix A, and the regulations and agency guidance documents listed in Appendix B.
USE OF DATA
The data on Form 1040 and its schedules will be used in computing the tax liability and IRS uses the information in determining that the items claimed are properly allowable. It is also used for general statistical use.
USE OF IMPROVED INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TO REDUCE BURDEN
We are currently offering electronic filing for these forms and schedules.
EFFORTS TO IDENTIFY DUPLICATION
The information obtained through this collection is unique and is not already available for use or adaptation from another source.
METHODS TO MINIMIZE BURDEN ON SMALL BUSINESSES OR OTHER SMALL ENTITIES
The IRS proactively works with both internal and external stakeholders to minimize the burden on small businesses, while maintaining tax compliance. The Agency also seeks input regarding the burden estimates from the public via notices and tax product instructions. The forms can be filed electronically, which further reduces any burden to small businesses.
CONSEQUENCES OF LESS FREQUENT COLLECTION ON FEDERAL PROGRAMS OR POLICY ACTIVITIES
Consequences of less frequent collection on federal programs or policy activities could consist of a decrease in the amount of taxes collected by the IRS, inaccurate and untimely filing of tax returns, and an increase in tax violations.
SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES REQUIRING DATA COLLECTION TO BE INCONSISTENT WITH GUIDELINES IN 5 CFR 1320.5(d)(2)
There are no special circumstances requiring data collection to be inconsistent with guidelines in 5 CFR 1320.5(d)(2).
CONSULTATION WITH INDIVIDUALS OUTSIDE OF THE AGENCY ON AVAILABILITY OF DATA, FREQUENCY OF COLLECTION, CLARITY OF INSTRUCTIONS AND FORMS, AND DATA ELEMENTS
In response to the Federal register notice dated July 16, 2025 (90 FR 32111), the IRS received no comment during the comment period for this collection of information.
EXPLANATION OF DECISION TO PROVIDE ANY PAYMENT OR GIFT TO RESPONDENTS
No payment or gift has been provided to any respondents.
ASSURANCE OF CONFIDENTIALITY OF RESPONSES
Generally, tax returns and tax return information are confidential as required by 26 U.S.C. 6103.
JUSTIFICATION OF SENSITIVE QUESTIONS
A privacy impact assessment (PIA) has been conducted for information collected under this request as part of the “Individual Master File (IMF)” system and a Privacy Act System of Records notice (SORN) has been issued for this system under IRS 24.030--Customer Account Data Engine Individual Master File, formerly Individual Master File, and IRS 34.037--IRS Audit Trail and Security Records System. The Internal Revenue Service PIAs can be found at https://www.irs.gov/privacy-disclosure/privacy-impact-assessments-pia.
Title 26 U.S.C. 6109 requires inclusion of identifying numbers in returns, statements, or other documents for securing proper identification of persons required to make such returns, statements, or documents and is the authority for social security numbers (SSNs) in IRS systems.
ESTIMATED BURDEN OF INFORMATION COLLECTION &
ESTIMATED TOTAL ANNUAL COST BURDEN TO RESPONDENTS
PRA Approval of Forms Used by Individual Taxpayers
Under the PRA, OMB assigns a control number to each ''collection of information'' that it reviews and approves for use by an agency. The PRA also requires agencies to estimate the burden for each
collection of information. Burden estimates for each control number are displayed in (1) PRA supporting statement that accompanies collections of information, (2) Federal Register notices, and (3) OMB's database of approved information collections.
This collection includes the income tax returns and related forms, schedules, attachments, and published guidance used by individual taxpayers to report and pay their income taxes.
RAAS Taxpayer Burden Model for Individual Taxpayers
Tax compliance burden is defined as the time and money taxpayers spend to comply with their tax filing responsibilities. Time-related activities include recordkeeping, tax planning, gathering tax materials, learning about the law, and completing and submitting the return. Out-of-pocket costs include expenses such as purchasing tax software, paying a third-party preparer, and printing and postage. Tax compliance burden does not include a taxpayer’s tax liability, economic inefficiencies caused by sub-optimal choices related to tax deductions or credits, or psychological costs.
The IRS uses the RAAS Taxpayer Burden Model for Individual Taxpayers (Individual Taxpayer Burden Model) to estimate the burden experienced by individual taxpayers when complying with Federal tax laws. The model is based on a survey of Tax Year 2023 individual taxpayers that was fielded in 2024 and 2025. The model is updated annually to account for technical, legislative, and agency adjustments.
The RAAS methodology for estimating burden focuses on the characteristics of activities undertaken by individual taxpayers in meeting their tax filing obligations. It is based on the primary drivers associated with observed individual taxpayer reporting burden. These include tax return preparation method (self-prepared with or without software, use of a paid preparer or tax professional, or use of Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) or Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE) programs), total income, type of filer (wage and investment or business), and the complexity of the individual’s income generated from assets and investments. Developments in tax law and changes in the tax forms and instructions are incorporated into the model as appropriate.
There is significant variation in taxpayer activity across different taxpayer groups. For example, non-business taxpayers are expected to have an average compliance burden of about 8 hours and $160, while business taxpayers are expected to have an average compliance burden of about 21 hours and $610. Similarly, tax preparation and other out-of-pocket costs vary extensively depending on the tax situation of the taxpayer, the type of software or professional preparer used, and geographic location.
Taxpayer Burden Estimates
Summary results for Fiscal Year 2026 using the Individual Taxpayer Burden Model estimation methodology are presented below. The data shown are the best forward-looking estimates available for individual income tax returns filed for Tax Year 2025. The burden estimates are based on statutory requirements as of November 20, 2025.
Total Burden Table
-
Table 1
Burden Estimates for U.S. Individual Income Tax Returns and Related Forms, Schedules, Attachments, and Published Guidance
Fiscal Year 2026
Fiscal Year 2025
Program Change Due to Technical Adjustment
Program Change Due to Legislative Adjustment
Program Change Due to Agency Adjustment
Fiscal Year 2026
Number of Respondents
168,800,000
1,300,000
0
0
170,100,000
Time (Hours)
2,129,000,000
(213,000,000)
32,000,000
0
1,948,000,000
Monetized Time
$44,997,000,000
($3,678,000,000)
$709,000,000
$0
$42,028,000,000
Out-of-Pocket Costs
$48,683,000,000
$175,000,000
$902,000,000
$0
$49,760,000,000
Total Monetized Burden*
$93,680,000,000
($3,503,000,000)
$1,611,000,000
$0
$91,788,000,000
Source: IRS:RAAS:KDA:BRDN (10-1-2025)
*Total Monetized Burden = Monetized Time + Out-of-Pocket Costs
Note: Reported time and cost burdens are national averages and do not necessarily reflect a “typical” case. Most taxpayers experience lower than average burden, with taxpayer burden varying considerably by taxpayer type.
Tax return data are used to calculate a monetization rate for individual taxpayers. We assign an after-tax hourly wage rate based on the taxpayer’s marginal tax rate, FICA tax rate (if applicable to income at the marginal rate) and Medicare tax rate. For self-employed taxpayers, changes in net income are controlled for by using a three-year average. A lower bound is set at the federal minimum wage rate. An upper bound is set using labor rates from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Occupational and Employment Wage Statistics (OEWS) for the major occupational group and detailed occupations relevant for each burden activity. This upper bound limitation is applied to take into account the fact that above a certain wage rate, taxpayers tend to use a paid preparer because the value of their time generally exceeds what they would pay a preparer to complete the return.
The following additional breakouts of average burden are provided for transparency in understanding the average estimated burden experienced by taxpayers.
-
Table 2
Individual Taxpayer Estimated Average Burden by Activity
Fiscal Year 2026
Percentage of Total Forms 1040
Average Time (Hours)
Average Out-of-Pocket Cost (Dollars)
Total Monetized Burden (Dollars)
Total Time
Record Keeping
Tax Planning
Form Completion
All Other
and Submission
All Taxpayers
100%
12
5
2
4
1
$290
$540
Type of Taxpayer
Nonbusiness*
71%
8
3
1
3
1
$160
$310
Business*
29%
21
10
4
5
2
$610
$1,100
Source: IRS:RAAS:KDA:BRDN (10-1-2025)
*A "business" filer files one or more of the following with Form 1040 or 1040-SR: Schedule C, E, F, or Form 2106. A "nonbusiness" filer does not file any of these schedules or forms with Form 1040 or 1040-SR.
Note: Dollars rounded to the nearest $10.
The average time and out-of-pocket costs listed in Table 2 represent the federal income tax compliance burden for individual taxpayers who will file a Tax Year 2025 Form 1040 federal income tax return as estimated using the Individual Burden Model estimation methodology.
-
Table 3
Individual Taxpayer Estimated Average Burden by Total Positive Income Quintile
Fiscal Year 2026
All Filers
Total Positive Income Quintiles
Average Time (Hours)
Average Out-of-Pocket Costs
Average Monetized Burden
0 to 20
7.7
$85
$148
20 to 40
9.7
$136
$242
40 to 60
10.1
$179
$328
60 to 80
11.1
$263
$488
80 to 100
19.1
$810
$1,506
Wage and Investment Filers
Total Positive Income Quintiles
Average Time (Hours)
Average Out-of-Pocket Costs
Average Monetized Burden
0 to 20
6.8
$69
$126
20 to 40
8.1
$115
$208
40 to 60
7.7
$145
$271
60 to 80
7.7
$201
$380
80 to 100
9.2
$373
$748
Self Employed Filers
Total Positive Income Quintiles
Average Time (Hours)
Average Out-of-Pocket Costs
Average Monetized Burden
0 to 20
10.9
$142
$232
20 to 40
16.7
$229
$390
40 to 60
18.1
$295
$520
60 to 80
18.6
$397
$721
80 to 100
28.0
$1,201
$2,185
Source IRS:RAAS:KDA:TBL (10-1-2025)
-
Table 4
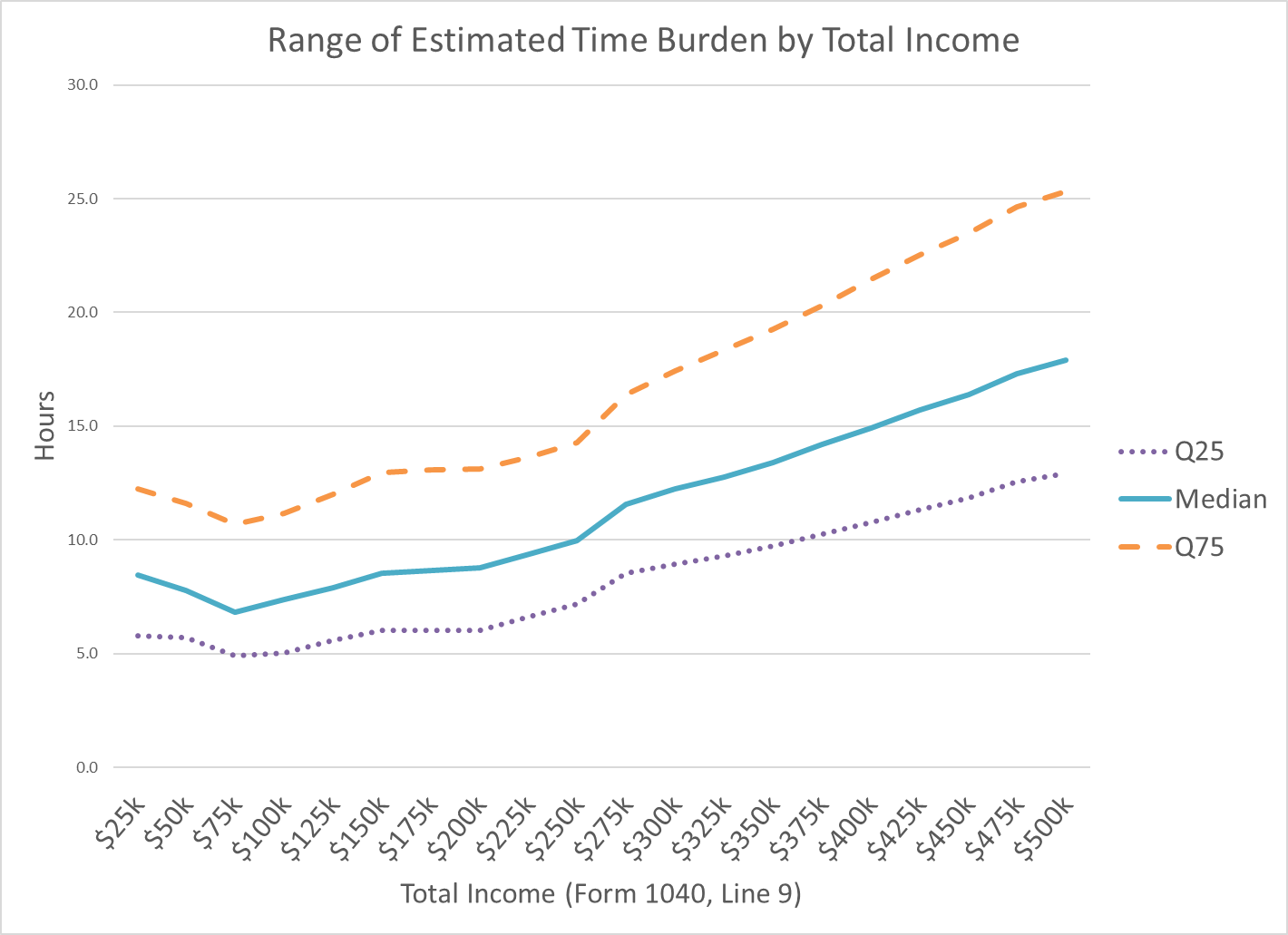
Individual Taxpayer Estimated Average and Median Burden by Total Income
Fiscal Year 2026
Average
Median
Time (Hours)
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Time (Hours)
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Under $25k
10.7
$125
8.5
$83
$25k to $50k
10.6
$165
7.8
$121
$50k to $75k
9.8
$199
6.8
$155
$75k to $100k
10.0
$250
7.4
$195
$100k to $125k
10.5
$303
7.9
$239
$125k to $150k
11.1
$352
8.5
$281
$150k to $175k
11.3
$403
8.7
$322
$175k to $200k
11.4
$454
8.8
$360
$200k to $225k
11.9
$520
9.4
$416
$225k to $250k
12.5
$583
10.0
$473
$250k to $275k
14.6
$707
11.6
$580
$275k to $300k
15.4
$797
12.2
$655
$300k to $325k
16.1
$876
12.8
$721
$325k to $350k
16.8
$951
13.4
$791
$350k to $375k
17.5
$1,021
14.2
$850
$375k to $400k
18.7
$1,109
14.9
$922
$400k to $425k
19.4
$1,177
15.7
$990
$425k to $450k
20.3
$1,244
16.4
$1,047
$450k to $475k
21.4
$1,340
17.3
$1,134
$475k to $500k
22.1
$1,402
17.9
$1,194
Source IRS:RAAS:KDA:BRDN (10-1-2025)
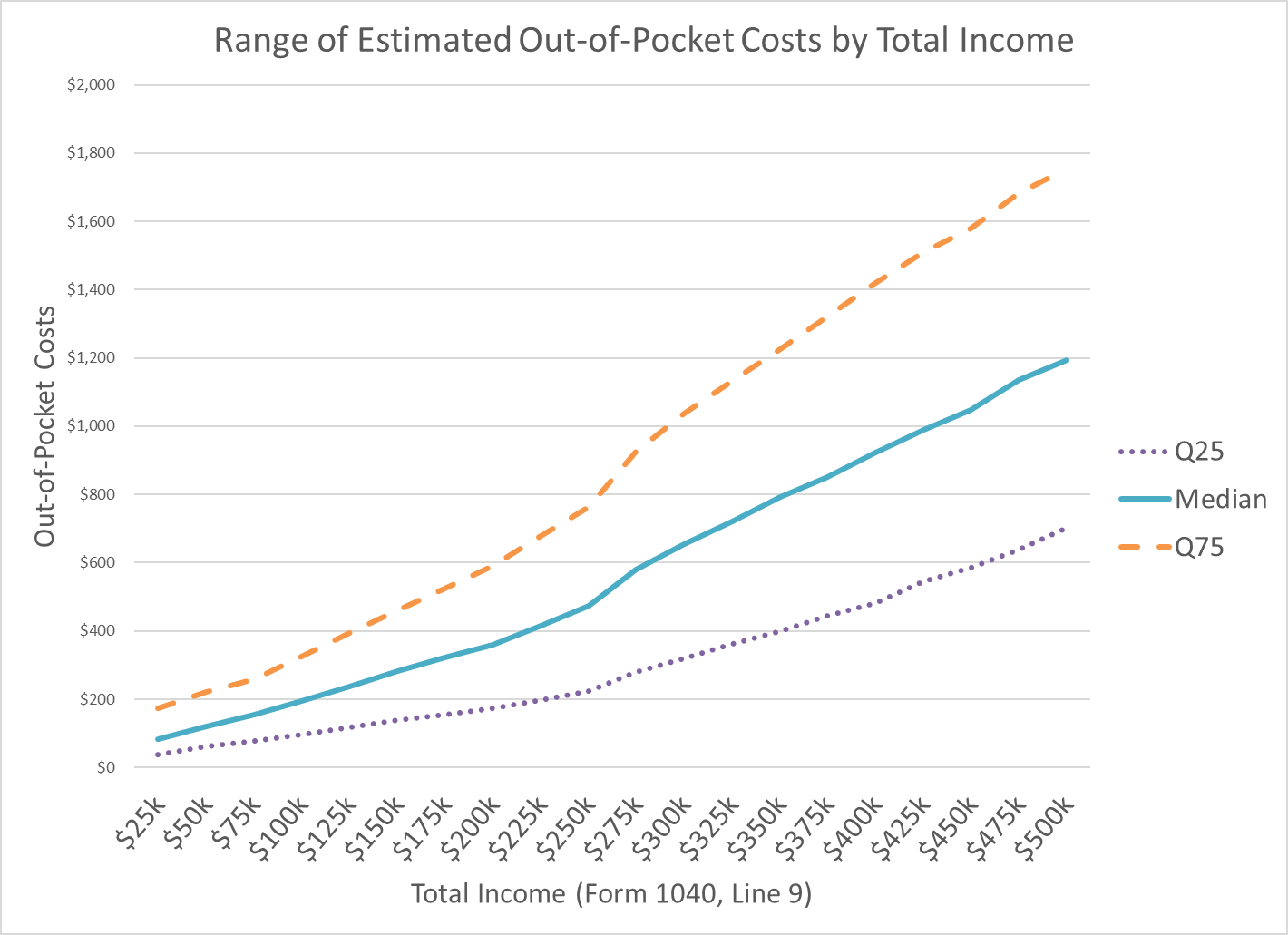
ESTIMATED ANNUALIZED COST TO THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT
The federal government cost estimate for product development is based on a model that considers the following three cost factors for each information product: aggregate labor costs for development, including annualized startup expenses, operating and maintenance expenses, and distribution of the product that collects the information. These costs do not include any activities such as taxpayer assistance and enforcement.
The government computes cost using a multi-step process. First, the government creates a weighted factor for the level of effort to create each information collection product based on variables, such as complexity, number of pages, type of product, and frequency of revision. Second, the total costs associated with developing the product such as labor cost, and operating expenses associated with the downstream impact such as support functions, are added together to obtain the aggregated total cost. Then, the aggregated total cost and factor are multiplied together to obtain the aggregated cost per product. Lastly, the aggregated cost per product is added to the cost of shipping and printing each product to IRS offices, National Distribution Center, libraries, and other outlets. The result is the government cost estimate per product.
The government cost estimate for this collection is summarized in the table below. See the attached Government Cost document in the supplementary documents section for more information.
Product |
Aggregate Cost per Product (factor applied) |
|
Print & Distribution |
|
Government Cost Estimate per Product |
All Forms attached* |
$ 13,921,860 |
+ |
$ 1,355,133 |
= |
$ 15,276,993 |
Total |
|
|
|
|
$ 15,276,993 |
Table costs are based on 2024 actuals obtained from IRS Chief Financial Office and Media and Publications *New product costs will be included in the next collection update. |
|||||
The government cost estimates for processing tax returns and performing related functions in the Submission Processing Campus(es) includes salaries and benefits only. Other costs such as real estate, programming, recruitment, equipment, and supplies are not included.
Estimated Filers |
Processing Cost - Paper Returns* |
|
Processing Cost - Electronic Returns* |
|
Government Cost Estimate |
170,100,000 |
$ 83,774,250 |
+ |
$ 37,166,850 |
= |
$ 120,941,100 |
Total |
|
|
|
|
$ 120,941,100 |
*Table costs estimates are based on FY2024 IRS Cost Estimate References. |
|||||
The total government cost estimate for this collection is $136,218,093.
REASONS FOR CHANGE IN BURDEN
The year-over-year change in burden is analyzed and reported by technical adjustments, legislative adjustments, and agency adjustments.
Changes Due to Technical Adjustment: The majority of the year-over year change in burden is due to technical adjustments. The table provided below breaks down the major changes by technical adjustment type.
Updates to FY2025 estimates resulted in a 1.6% reduction in total monetized burden. This net reduction includes a minor increase in the aggregate filer count but is primarily driven by the composition of the underlying tax return data and revised legislative and agency estimates based on filing data.
The incorporation of new survey data and the associated updates to the Individual Taxpayer Burden Model resulted in a 4.5% decrease in total monetized burden. This is primarily driven by a 5.6% reduction in time burden.
The Fiscal Year 2026 population adjustments transition the underlying data file from Fiscal Year 2025 to Fiscal Year 2026 which includes aging the data for macroeconomic factors and adjusting weights to account for changes in the year-over-year population differences. A forecasted increase in filers is expected to lead to an increase in time and out-of-pocket costs. Forecasted changes in macroeconomic factors are also expected to lead to increases in average monetized time, out-of-pocket costs, and total monetized burden. These changes in the filer population and macroeconomic factors are expected to increase total monetized burden by 2.4%. This includes a 0.1% increase in time burden and a 2.4% increase in out-of-pocket costs.
Altogether, these technical adjustments reduced total monetized burden by 3.7%. This net decrease includes a 0.8% increase in the filer population and decreases in time burden of 10.0% and out-of-pocket costs of 0.4%.
-
Table 5
Individual Taxpayer Program Change Due to Technical Adjustment
Fiscal Year 2026
Change in Respondents
Change in Time (Hours)
Change in Monetized Time
Change in Out-of-Pocket Costs
Change in Total Monetized Burden*
Fiscal Year 2025 Updates**
100,000
(102,000,000)
($2,684,000,000)
$1,189,000,000
($1,495,000,000)
Update to Burden Survey Data and Model
0
(113,000,000)
(1,960,000,000)
(2,179,000,000)
(4,139,000,000)
Projection to Fiscal Year 2026***
1,200,000
2,000,000
$966,000,000
$1,165,000,000
$2,131,000,000
Total Technical Adjustments
1,300,000
(213,000,000)
($3,678,000,000)
$175,000,000
($3,503,000,000)
Source: IRS:RAAS:KDA:BRDN (10-1-2025)
*Change in Total Monetized Burden = Change in Monetized Time + Change in Out-of-Pocket Costs
**lncludes updated population counts, macroeconomic adjustments, and updated tax return data
***lncludes updated population counts and macroeconomic adjustments
Changes due to Legislative Adjustment: There are two legislative adjustments that may have a material effect on burden relative to a current policy baseline. These include new 1099-DA reporting requirements and changes associated with Pub. L. 119-21 (One Big Beautiful Bill Act).
The total monetized burden is expected to increase by 0.3% due to individuals receiving Form 1099-DA. This includes a 0.3% increase to both time burden and out-of-pocket costs.
The overall impact of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act is a net increase in total monetized burden of 1.5%. The net increase consists of a net increase in time burden of 1.3% and out-of-pocket costs of 1.6% and is driven by increases in burden associated with Sections 70103 (Termination of Deduction for Personal Exemptions other than Temporary Senior Deduction , 70104 (Extension and Enhancement of Increased Child Tax Credit),) 70120 (Limitation on Individual Deductions for Certain State and Local Taxes, Etc.), 70201 (No Tax on Tips), 70202 (No tax on Overtime), and 70203 (No Tax on Car Loan Interest) and decreases in burden associated with Sections 70433 (Increase in Threshold for Requiring Information Reporting with Respect to Certain Payees), 70501 (Termination of Previously-Owned Clean Vehicle Credit), and 70502 (Termination of Clean Vehicle Credit).
Altogether, adjustments due to legislative changes are expected to increase total monetized burden by 1.8%. This includes a 1.7% increase in time burden and a 1.8% increase in out-of-pocket costs.
-
Table 6
Individual Taxpayer Program Change Due to Legislative Adjustment
Fiscal Year 2026
Change in Respondents
Change in Time (Hours)
Change in Monetized Time
Change in Out-of-Pocket Costs
Change in Total Monetized Burden*
New 1099-DA Reporting Requirements
0
6,100,000
$122,000,000
$141,000,000
$263,000,000
Pub. L. 119-21 (One Big Beautiful Bill Act)
0
25,900,000
$587,000,000
$761,000,000
$1,348,000,000
Total Legislative Adjustments
0
32,000,000
$709,000,000
$902,000,000
$1,611,000,000
Source: IRS:RAAS:KDA:BRDN (10-1-2025)
*Change in Total Monetized Burden = Change in Monetized Time + Change in Out-of-Pocket Costs
Changes due to Agency Adjustment: There were no independent and significant year-over-year Agency changes impacting the burden calculations for this collection.
ICR Summary of Burden
Table 7 |
|
||||||
Burden Estimates for U.S. Individual Income Tax Returns and Related Forms, Schedules, Attachments, and Published Guidance |
|
||||||
Fiscal Year 2026 |
|
||||||
|
Requested |
Program Change Due to Agency Adjustment |
Program Change Due to Legislative Adjustment |
Program Change Due to Technical Adjustment |
Program Change Due to Potential Violation of the PRA |
Previously Approved |
|
Number of Respondents |
170,100,000 |
0 |
0 |
1,300,000 |
0 |
168,800,000 |
|
Time (Hours) |
1,948,000,000 |
0 |
32,000,000 |
(213,000,000) |
0 |
2,129,000,000 |
|
Monetized Time |
$42,028,000,000 |
$0 |
$709,000,000 |
($3,678,000,000) |
$0 |
$44,997,000,000 |
|
Out-of-Pocket Costs |
$49,760,000,000 |
$0 |
$902,000,000 |
$175,000,000 |
$0 |
$48,683,000,000 |
|
Total Monetized Burden* |
$91,788,000,000 |
$0 |
$1,611,000,000 |
($3,503,000,000) |
$0 |
$93,680,000,000 |
|
Source: IRS:RAAS:KDA:BRDN (10-1-2025) |
|
||||||
*Total Monetized Burden = Monetized Time + Out-of-Pocket Costs |
|
||||||
Note: Reported time and cost burdens are national averages and do not necessarily reflect a “typical” case. Most taxpayers experience lower than average burden, with taxpayer burden varying considerably by taxpayer type. |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
See the attached table for a sample of the various changes made to tax forms to comply with the 2025 Technical, Legislative, and Agency Adjustments.
PLANS FOR TABULATION, STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND PUBLICATION
The intent of this collection is to collect data in areas of income, gains, losses, deductions, credits, and to figure the income tax liability of a taxpayer. There are no plans for the IRS to publish the information collected.
REASONS WHY DISPLAYING THE OMB EXPIRATION DATE IS INAPPROPRIATE
The IRS believes that displaying the OMB expiration date is inappropriate because it could cause confusion by leading taxpayers to believe that the forms and regulations expire as of the expiration date. Taxpayers are not likely to be aware that the IRS intends to request renewal of the OMB approval and obtain a new expiration date before the old one expires.
EXCEPTIONS TO THE CERTIFICATION STATEMENT
There are no exceptions to the certification statement.
Appendix-A: Forms and Schedules
Form No. |
Form Name |
1040 |
U.S. Individual Income Tax Return |
Schedule 1 (1040) |
Additional Income and Adjustments to Income |
Schedule 1-A (1040) |
Additional Deductions |
Schedule 2 (1040) |
Additional Taxes |
Schedule 3 (1040) |
Additional Credits and Payments |
1040-C |
U.S. Departing Alien Income Tax Return |
1040-X |
Amended U.S. Individual Income Tax Return |
1040-NR |
U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return |
Schedule NEC (1040-NR) |
Tax on Income Not Effectively Connected with a U.S. Trade or Business |
Schedule A (1040-NR) |
Itemized Deductions |
Schedule OI (1040-NR) |
Other Information |
Schedule P (1040NR) |
Gain or Loss of Foreign Persons from Sale or Exchange of Certain Partnership Interests |
1040-SR |
U.S. Tax Return for Seniors |
1040-SS |
U.S. Self-Employment Tax Return (Including the Additional Child Tax Credit for Bona Fide Residents of Puerto Rico) |
Schedule A (1040) |
Itemized Deductions |
Schedule B (1040) |
Interest and Ordinary Dividends |
Schedule C (1040) |
Profit or Loss from Business |
Schedule D (1040) |
Capital Gains and Losses |
Schedule E (1040) |
Supplemental Income and Loss |
Schedule EIC (1040) |
Earned Income Credit |
Schedule F (1040) |
Profit or Loss from Farming |
Schedule H (1040) |
Household Employment Taxes |
Schedule J (1040) |
Income Averaging for Farmers and Fishermen |
Schedule LEP (1040) |
Request for Change in Language Preference |
Schedule R (1040) |
Credit for the Elderly or the Disabled |
Schedule SE (1040) |
Self-Employment Tax |
1040-V |
Payment Voucher |
1040-ES/OCR |
Estimated Tax for Individuals (Optical Character Recognition with Form 1040V) |
1040-ES |
Estimate Tax for Individuals |
1040-ES (NR) |
U.S. Estimated Tax for Nonresident Alien Individuals |
Schedule 8812 (1040) |
Credits for Qualifying Children and Other Dependents |
172 |
Net Operating Losses (NOLs) for Individuals, Estates, and Trusts |
461 |
Limitation on Business Losses |
673 |
Statement for Claiming Exemption from Withholding on Foreign Earned Income Eligible for the Exclusion(s) Provided by Section 911 |
926 |
Return by a U.S. Transferor of Property to a Foreign Corporation |
965-A |
Individual Report of Net 965 Tax Liability |
965-C |
Transfer Agreement Under 965(h)(3) |
970 |
Application to Use LIFO Inventory Method |
972 |
Consent of Shareholder to Include Specific Amount in Gross Income |
982 |
Reduction of Tax Attributes Due to Discharge of Indebtedness (and Section 1082 Basis Adjustment) |
1045 |
Application for Tentative Refund |
1062 |
Deferral of Tax on Gain From the Sale or Exchange of Qualified Farmland Property to Qualified Farmers |
Schedule A (1062) |
Section 1062 Gain From the Sale or Exchange of Qualified Farmland Property to a Qualified Farmer |
1116 |
Foreign Tax Credit (Individual, Estate, or Trust) |
Schedule B (1116) |
Foreign Tax Carryover Reconciliation Schedule |
Schedule C (1116) |
Foreign Tax Redetermination |
1118 |
Foreign Tax Credit - Corporations |
1127 |
Application for Extension of Time for Payment of Tax Due to Undue Hardship |
1128 |
Application to Adopt, Change or Retain a Tax Year |
1310 |
Statement of Person Claiming Refund Due a Deceased Taxpayer |
2106 |
Employee Business Expenses |
2120 |
Multiple Support Declaration |
2210 |
Underpayment of Estimated Tax by Individuals, Estates, and Trusts |
2210-F |
Underpayment of Estimated Tax by Farmers and Fishermen |
2350 |
Application for Extension of Time to File U.S. Income Tax Return |
2441 |
Child and Dependent Care Expenses |
2555 |
Foreign Earned Income |
3115 |
Application for Change in Accounting Method |
3468 |
Investment Credit |
3520 |
Annual Return to Report Transactions with Foreign Trusts and Receipt of Certain Foreign Gifts |
3520-A |
Annual Information Return of Foreign Trust With a U.S. Owner |
3800 |
General Business Credit |
Schedule A (3800) |
Transfer Election Statement |
3903 |
Moving Expenses |
4136 |
Credit for Federal Tax Paid on Fuels |
Schedule A (4136) |
Business Activity Report for Credit for Federal Tax Pail on Fuels |
4137 |
Social Security and Medicare Tax on Unreported Tip Income |
4255 |
Recapture of Investment Credit |
4361 |
Application for Exemption from Self-Employment Tax for Use by Ministers, Members of Religious Orders, and Christian Science Practitioners |
4562 |
Depreciation and Amortization (Including Information on Listed Property) |
4563 |
Exclusion of Income for Bona Fide Residents of American Samoa |
4684 |
Causalities and Thefts |
4797 |
Sale of Business Property |
4835 |
Farm Rental Income and Expenses |
4852 |
Substitute for Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement or Form 1099-R, Distributions from Pensions, Annuities, Retirement or Profit-Sharing Plans, IRAs, Insurance Contracts, etc. |
4868 |
Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return |
4952 |
Investment Interest Expense Deduction |
4970 |
Tax on Accumulation Distribution of Trusts |
4972 |
Tax on Lump-Sum Distributions |
5074 |
Allocation of Individual Income Tax to Guam or the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) |
5213 |
Election to Postpone Determination as to Whether the Presumption Applies that an Activity is Engaged in for Profit |
5329 |
Additional Taxes on Qualified Plans (Including IRAs) and Other Tax-Favored Accounts |
5405 |
Repayment of the First-Time Homebuyer Credit |
5471 |
Information Return of U.S. Persons with Respect to Certain Foreign Corporations |
Schedule J (5471) |
Accumulated Earnings and Profits (E&P) of Controlled Foreign Corporations |
Schedule M (5471) |
Transactions Between Controlled Foreign Corporation and Shareholders or Other Related Persons |
Schedule O (5471) |
Organization or Reorganization of Foreign Corporation, and Acquisitions and Dispositions of its Stock |
5695 |
Residential Energy Credits |
5713 |
International Boycott Report |
Schedule A (5713) |
International Boycott Factor (Section 999(c)(1)) |
Schedule B (5713) |
Specifically Attributable Taxes and Income (Section 999(c)(2)) |
Schedule C (5713) |
Tax Effect of the International Boycott Provisions |
5884 |
Work Opportunity Credit |
5884-A |
Employee Retention Credit |
6198 |
At-Risk Limitations |
6251 |
Alternative Minimum Tax-Individuals |
6252 |
Installment Sale Income |
6478 |
Biofuel Producer Credit |
6765 |
Credit for Increasing Research Activities |
6781 |
Gains and Losses from Section 1256 Contracts and Straddles |
7203 |
S Corporation Shareholder Stock and Debt Basis Limitations |
7204 |
Consent to Extend the Time to Assess Tax Related to Contested Foreign Income Taxes-Provisional Foreign Tax Credit Agreement |
7205 |
Energy Efficient Commercial Buildings Deduction |
7206 |
Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction |
7207 |
Advanced Manufacturing Production Credit |
7210 |
Clean Hydrogen Production Credit |
7211 |
Clean Electricity Production Credit |
7213 |
Nuclear Power Production Credit |
7217 |
Partner’s Report of Property Distributed by a Partnership |
7218 |
Clean Fuel Production Credit |
7220 |
Prevailing Wage and Apprenticeship (PWA) Verification and Corrections |
8082 |
Notice of Inconsistent Treatment or Administrative Adjustment Request (AAR) |
8275 |
Disclosure Statement |
8275-R |
Regulation Disclosure Statement |
8283 |
Noncash Charitable Contributions |
8332 |
Release/ Revocation of Release of Claim to Exemption for Child by Custodial Parent |
8379 |
Injured Spouse Allocation |
8396 |
Mortgage Interest Credit |
8453 |
U.S. Individual Income Tax Transmittal for an IRS e-file Return |
8453-TR |
E-file Declaration or Authorization for Form 1045/1139 |
8582 |
Passive Activity Loss Limitation |
8582-CR |
Passive Activity Credit Limitations |
8586 |
Low-Income Housing Credit |
8594 |
Asset Acquisition Statement Under Section 1060 |
8606 |
Nondeductible IRAs |
8609-A |
Annual Statement for Low-Income Housing Credit |
8611 |
Recapture of Low-Income Housing Credit |
8615 |
Tax for Certain Children Who Have Unearned Income |
8621 |
Information Return by a Shareholder of a Passive Foreign Investment Company or Qualified Electing Fund |
8621-A |
Return by a Shareholder Making Certain Late Elections to End Treatment as a Passive Foreign Investment Company |
8689 |
Allocation of Individual Income Tax to the U.S. Virgin Islands |
8697 |
Interest Computation Under the Look-Back Method for Completed Long-Term Contracts |
8801 |
Credit for Prior Year Minimum Tax-Individuals, Estates, and Trusts |
8814 |
Parents' Election to Report Child's Interest and Dividends |
8815 |
Exclusion of Interest from Series EE and I U.S. Savings Bonds Issued After 1989 |
8818 |
Optional Form to Record Redemption of Series EE and I U.S. Savings Bonds Issued After 1989 |
8820 |
Orphan Drug Credit |
8824 |
Like-Kind Exchanges |
8825 |
Rental Real Estate Income and Expenses of a Partnership or an S Corporation |
Schedule A (8825) |
Rental Real Estate Other Deductions |
8826 |
Disabled Access Credit |
8828 |
Recapture of Federal Mortgage Subsidy |
8829 |
Expenses for Business Use of Your Home |
8830 |
Enhanced Oil Recovery Credit |
8833 |
Treaty-Based Return Position Disclosure Under Section 6114 or 7701(b) |
8834 |
Qualified Electric Vehicle Credit |
8835 |
Renewable Electricity, Refined Coal, and Indian Coal Production Credit |
8838 |
Consent to Extend the Time to Assess Tax Under Section 367-Gain Recognition Agreement |
8838-P |
Consent To Extend the Time To Assess Tax Pursuant to the Gain Deferral Method (Section 721(c)) |
8839 |
Qualified Adoption Expenses |
8840 |
Closer Connection Exception Statement for Aliens |
8843 |
Statement for Exempt Individuals and Individuals with a Medical Condition |
8844 |
Empowerment Zone Employment Credit |
8845 |
Indian Employment Credit |
8846 |
Credit for Employer Social Security and Medicare Taxes Paid on Certain Employee Tips |
8853 |
Archer MSA’s and Long-Term Care Insurance Contracts |
8854 |
Initial and Annual Expatriation Statement |
8858 |
Information Return of U.S. Persons with Respect to Foreign Disregarded Entities (FDEs) and Foreign Branches (FBs) |
Schedule M (8858) |
Transactions Between Foreign Disregarded Entity (FDE) or Foreign Branch (FB)and the Filer or Other Related Entities |
8859 |
Carryforward of the District of Columbia First-Time Homebuyer Credit |
8862 |
Information to Claim Earned Income Credit After Disallowance |
8863 |
Education Credits (American Opportunity and Lifetime Learning Credits) |
8864 |
Biodiesel and Renewable Diesel Fuels Credit |
8865 |
Return of U.S. Persons with Respect to Certain Foreign Partnerships |
Schedule K-1 (8865) |
Partner's Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc. |
Schedule K-2 (8865) |
Partners' Distributive Share Items - International |
Schedule K-3 (8865) |
Partner's Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc. International |
Schedule O (8865) |
Transfer of Property to a Foreign Partnership (Under section 6038B) |
Schedule P (8865) |
Acquisitions, Dispositions, and Changes of Interests in a Foreign Partnership |
8866 |
Interest Computation Under the Look-Back Method for Property Depreciated Under the Income Forecast Method |
8867 |
Paid Preparer's Due Diligence Checklist |
8873 |
Extraterritorial Income Exclusion |
8874 |
New Markets Credit |
8878 |
IRS e-file Signature Authorization for Form 4868 or Form 2350 |
8879 |
IRS e-file Signature Authorization |
8880 |
Credit for Qualified Retirement Savings Contributions |
8881 |
Credit for Small Employer Pension Plan Startup Costs |
8882 |
Credit for Employer-Provided Child Care Facilities and Services |
8883 |
Asset Allocation Statement Under Section 338 |
8886 |
Reportable Transaction Disclosure Statement |
8888 |
Allocation of Refund (Including Savings Bond Purchases) |
8889 |
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) |
8896 |
Low Sulfur Diesel Fuel Production Credit |
8898 |
Statement for Individuals Who Begin or End Bona Fide Residence in a U.S. Possession |
8900 |
Qualified Railroad Track Maintenance Credit |
8903 |
Domestic Production Activities Deduction |
8904 |
Credit for Oil and Gas Production From Marginal Wells |
8906 |
Distilled Spirits Credit |
8908 |
Energy Efficient Home Credit |
8910 |
Alternative Motor Vehicle Credit |
8911 |
Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit |
Schedule A (8911) |
Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property |
8912 |
Credit to Holders of Tax Credit Bonds |
8915-D |
Qualified 2019 Disaster Retirement Plan Distributions and Repayments |
8915-F |
Qualified Disaster Retirement Plan Distributions and Repayments |
8919 |
Uncollected Social Security and Medicare Tax on Wages |
8923 |
Mine Rescue Team Training Credit |
8925 |
Report of Employer-Owned Life Insurance Contracts |
8932 |
Credit for Employer Differential Wage Payments |
8933 |
Carbon Oxide Sequestration Credit |
Schedule A (8933) |
Disposal or Enhanced Oil Recovery Owner |
Certification |
|
Schedule B (8933) |
Disposal Operator Certification |
Schedule C (8933) |
Enhanced Oil Recovery Operator Certification |
Schedule D (8933) |
Recapture Certification |
Schedule E (8933) |
Election Certification |
Schedule F (8933) |
Utilization Certification |
8936 |
Clean Vehicle Credits |
Schedule A (8936) |
Clean Vehicle Credit Amount |
8938 |
Statement of Specified Foreign Financial Assets |
8941 |
Credit for Small Employer Health Insurance Premiums |
8949 |
Sales and other Dispositions of Capital Assets |
8958 |
Allocation of Tax Amounts Between Certain Individuals in Community Property States |
8960 |
Net Investment Income Tax-Individuals, Estates, and Trusts |
8962 |
Premium Tax Credit (PTC) |
8964-ELE |
Section 987 Elections |
8964-TRA |
Section 987 Transition Information |
8978 |
Partner’s Additional Reporting Year Tax |
Schedule A (8978) |
Partner’s Additional Reporting Year Tax (Schedule of Adjustments) |
8990 |
Limitation on Business Interest Expense Under Section 163(j) |
8992 |
U.S. Shareholder Calculation of Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI) |
Schedule A (8992) |
Schedule of Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC) Information To Compute Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI) |
8993 |
Section 250 Deduction for Foreign Derived Intangible Income (FDII) and Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI) |
8994 |
Employer Credit for Paid Family and Medical Leave |
8995 |
Qualified Business Income Deduction Simplified Computation |
8995-A |
Qualified Business Income Deduction |
Schedule A (8995-A) |
Specified Service Trades or Businesses |
Schedule B (8995-A) |
Aggregation of Business Operations |
Schedule C (8995-A) |
Loss Netting And Carryforward |
Schedule D (8995-A) |
Special Rules for Patrons of Agricultural or Horticultural Cooperatives |
8997 |
Initial and Annual Statement of Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF) Investments |
9000 |
Alternative Media Preference |
9465 |
Installment Agreement Request |
15620 |
Section 83(b) Election |
W-4 |
Employee's Withholding Certificate |
W-4 P |
Withholding Certificate for Pension or Annuity Payments |
W-4 S |
Request for Federal Income Tax Withholding from Sick Pay |
W-4 V |
Voluntary Withholding Request |
W-4 R |
Withholding Certificate for Retirement Payments Other Than Pensions or Annuities |
W-7 |
Application for IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number |
W-7 A |
Application for Taxpayer Identification Number for Pending U.S. Adoptions |
W-7 (COA) |
Certificate of Accuracy for IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number |
Form T (Timber) |
Forest Activities Schedule |
Appendix-B: Regulations and Agency Guidance Documents
Treasury Regulations |
1.23-5
1.31.2
1.37-2 and 3
1.41-4
1.41-4A
1.43-2
1.44A-3
1.52-4
1.61-15
1.63-1
1.64(c)6
1.71-1
1.72-4 thru 18
1.79-2 and 3
1.83-2 thru 5
1.105
1.151-1
1.152-4 and 4T
1.162-24
1.163-10T
1.166-10
1.170-1 and 2
1.170A-2 and 8
1.172
1.180-2
1.182-6
1.190-3
1.197-2
1.213-1
1.215-1
1.254-1
1.265-1
1.274-5T and 6T
1.280A-3
1.280F-3T
1.302-4
1.307-2
1.333-1
1.351-3
1.383-1
1.442-1
1.446-1
1.451-5 thru 7
1.454-1
1.461-1
1.466-1
1.551-4
1.612-4
1.642(c)-5 and 6
1.702-1
1.706-1
1.736-1
1.743-1
1.751-1
1.752-7
1.852-7 and 9
1.861-4
1.931-1
1.934-1
1.935-1
1.937-1
1.1012-1
1.1041-1T
1.1081-11
1.1101-4
1.1211-1
1.1212-1
1.1231-2
1.1232-3
1.1248-7
1.1251-2
1.1254-1 and 3
1.1304-1 thru 5
1.1311(a)-1
1.1383-1
1.1385-1
1.1402(a)-2,5,11,15
1.1402(c)-2
1.1402(e)(2)-1
1.1402(f)-1
1.6001-1
1.6060-1
1.6107-1
1.6109-1 and 2
1.6011-1
1.6012-1
1.6013-1, 6, 7
1.6017-1
1.6060-1
1.6072-1
1.6107-1
1.6109-1
1.6151-1
1.6695-1
1.6696-1
1.9100-1
5c.0
7
16A.126-2
31.6011(a)-1 and 7
301.6110-3 and 5
301.6316-4 thru 6
301.6361-1 and 3
301.6501
301.6501(d)
301.6905-1
301.7216-2
301.9001-2 and 3
-
Document
Title
Notice 2006-52
Deduction for Energy Efficient Commercial Buildings
Notice 2008-40
Amplification of Notice 2006–52; Deduction for Energy Efficient Commercial Buildings
Notice 2024-60
Required Procedures to Claim a Section 45Q Credit for Utilization of Carbon Oxide
Publication 972 Tables
Child Tax Credit
Rev. Proc. 2004-12
Section 35. —Health Insurance Costs of Eligible Individuals
Rev. Proc. 2019-38
Trade or Business
Rev. Proc. 2024-09
Changes in accounting periods and in methods of accounting
Rev. Proc. 2024-23
Changes in accounting periods and in methods of accounting
Rev. Proc. 2025-23
Changes in accounting periods and in methods of accounting
Rev. Proc. 2025-28
Changes in accounting periods and in methods of accounting
TD 8400
Taxation of Gain or Loss from Certain Nonfunctional Currency Transactions (Section 988 Transactions)
TD 8865
Amortization of Intangible Property
TD 9207
Assumption of Partner Liabilities
TD 9764
Section 6708 Failure To Maintain List of Advisees With Respect to Reportable Transactions
TD 9408
Dependent Child of Divorced or Separated Parents or Parents Who Live Apart
TD 9902
Guidance Under Sections 951A and 954 Regarding Income Subject to a High Rate of Foreign Tax
TD 9920
Income Tax Withholding on Certain Periodic Retirement and Annuity Payments Under Section 3405(a)
TD 9924
Income Tax Withholding from Wages
TD 9959
Guidance Related to the Foreign Tax Credit; Clarification of Foreign-Derived Intangible Income
TD 9993
Transfer of Certain Credits
TD 9998
Increased Amounts of Credit or Deduction for Satisfying Certain Prevailing Wage and Registered Apprenticeship Requirements
TD 9999
Statutory Disallowance of Deductions for Certain Qualified Conservation Contributions Made by Partnerships and S Corporations
TD 10015
Definition of Energy Property and Rules Applicable to the Energy Credit
TD 10016
Taxable Income or Loss and Currency Gain or Loss With Respect to a Qualified Business Unit
TD 10022
Classification of Digital Content Transactions and Cloud Transactions
TD 10023
Credit for Production of Clean Hydrogen and Energy Credit
TD 10024
Section 45Y Clean Electricity Production Credit and Section 48E Clean Electricity Investment Credit
TD 10025
Guidance on Clean Electricity Low-Income Communities Bonus Credit Amount Program
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2025-12-16 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy